abnormal gain
Improvement on the accepted or normal level of loss associated with a production activity. It is isolated as a period entry rather than as an adjustment to product cost.
abnormal loss
Any loss in excess of the normal loss allowance. It is isolated as a period entry rather than as a component of product cost.
absorbed overhead
Overhead attached to products or services by means of an absorption rate, or rates.
under- or over-absorbed overhead: The difference between overhead incurred and overhead absorbed, using an estimated rate, in a given period.
If overhead absorbed is less than that incurred there is under-absorption; if overhead absorbed is more than that incurred there is over-absorption. Over- and under-absorptions are treated as period cost adjustments.
See Figure 1.1.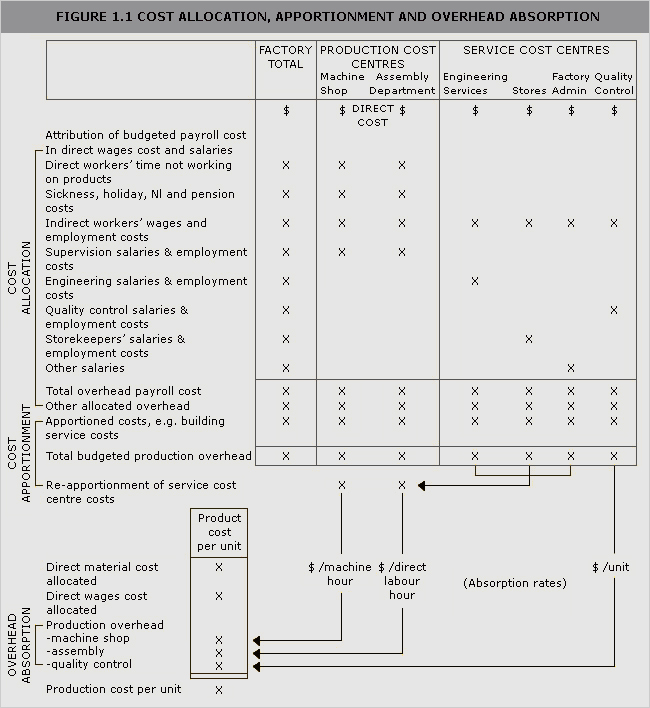
absorption rate
See overhead absorption rate.
account
Structured record of transactions in monetary terms kept as part of an accounting system. This may be a simple list, or entries on a debit and credit basis, maintained either manually or as a computer record.
See Figure 3.1 for an illustration of the relationship of accounts.
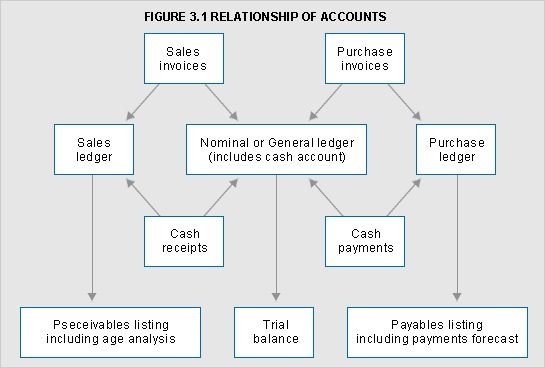
cash account: Record of receipts and payments of cash, cheques or other forms of money transfer.
nominal account: Record of revenues and expenditures, liabilities and assets classified by their nature, for example sales, rent, rates, electricity, wages and share capital. These are sometimes referred to as impersonal accounts.
personal account: Record of amounts receivable from or payable to a person or an entity. A collection of these accounts is known as a sales/debtor ledger, or a purchases/creditors ledger. In the US the terms receivables ledger and payables ledger are used and are consistent with IAS 1.
accounting manual
Collection of accounting instructions governing the responsibilities of persons, and the procedures, forms and records relating to the preparation and use of accounting data. There can be separate manuals for the constituent parts of the accounting system, such as a budget manual or cost accounting manual.
accounting period
Time period covered by the accounting statements of an entity. There may be different time periods for different accounting statements, for example, management accounts may be for four- or five-week periods to coincide with a thirteen-week financial accounting period.
accounting policies
Specific principles, bases, conventions, rules and practices applied by an entity in preparing and presenting its financial statements (IAS 8)
accounting reference period
Period for which an entity prepares its financial statements. This period is normally, though not necessarily, twelve months. Also used for taxation where it represents the period upon which adjusted profits, for corporation/income tax purposes, is based.
accounting standards
See International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs), which includes International Accounting Standards (IASs). In the UK there are Statements of Standard Accounting Practice (SSAPs) and Financial Reporting Standards (FRSs). All International and UK Accounting Standards are listed in Appendices 1 and 2.
Accounting Standards Board (ASB)
UK standard-setting body established to develop, issue and withdraw accounting standards. Its aims are to establish and improve standards of financial accounting and reporting, for the benefit of users, preparers and auditors of financial information (ASB). It will work with and influence the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) in addressing UK accounting issues.
accounts, integrated
Set of accounting records that integrates both financial and cost accounts using a common input of data for all accounting purposes.
accounts, interlocking
Set of accounting records where the cost and financial accounts are distinct, the two being kept continuously in agreement by the use of control accounts or reconciled by other means.
accruals basis of accounting
Effects of transactions and other events are recognised in financial statements when they occur and not when cash and cash equivalents are received or paid (IASB Framework).
acquisition date
Date on which the acquirer effectively obtains control of the acquiree (IFRS 3).
activities, hierarchy of
Classification of activities by level of organisation, for example unit, batch, product sustaining and facility sustaining.
activity, batch level
Activity (such as setting up machines) where volume varies directly with the number of batches of output but is independent of the number of units in a batch.
See activities, hierarchy of.
activity cost pool
Aggregation of all costs related to a specific activity.
activity driver
Transaction that causes an activity. For example, receipt of a sales order sets in train the order processing activity.
activity driver analysis
Identification and evaluation of the activity drivers used to trace the cost of activities to cost objects.
activity, facility sustaining
Activity undertaken to support the organisation as a whole, and which cannot be logically linked to individual units of output. Accounting is a facility sustaining activity.
See activities, hierarchy of.
activity, product sustaining
Activity undertaken to develop or sustain a product (or service). Product sustaining costs are linked to the number of products or services, not to the number of units produced.
activity-based budgeting
Method of budgeting based on an activity framework and utilising cost driver data in the budget setting and variance feedback processes.
activity-based costing (ABC)
Approach to the costing and monitoring of activities which involves tracing resource consumption and costing final outputs. Resources are assigned to activities, and activities to cost objects based on consumption estimates. The latter utilise cost drivers to attach activity costs to outputs.
See Figure 1.2.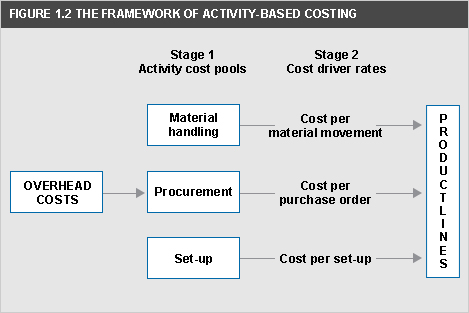
activity-based costing, time-driven (time-driven ABC)
Approach to ABC based on the time required for each unit activity. The method avoids the use of interviews with operating managers in order to estimate percentage of time spent on different areas of work. It is claimed that 'time-driven ABC' based on 'time per transactional activity' is simpler to install and update and can highlight unused capacity.
activity-based management (ABM)
operational ABM: Actions, based on activity driver analysis, that increase efficiency, lower costs and/or improve asset utilisation.
strategic ABM: Actions, based on activity-based cost analysis, that aim to change the demand for activities so as to improve profitability.
actuarial assumptions
An entity's unbiased best estimates of the demographic and financial variables that will determine the ultimate cost of providing post employment benefits (IAS 19).
adjusted present value (APV)
Net present value of an asset that also takes account of any financing side effects.
administrative expenses
Cost of management, secretarial, accounting and other services which cannot be related to the separate production, marketing or research and development functions. These expenses are reported in the income statement.
ad valorem (duty)
Duty based on the value of a product or service.
allocate
To assign a whole item of cost, or of revenue, to a single cost unit, centre, account or time period. In the US, 'allocate' does not have this precise meaning, it is used more generally to refer to the whole process of overhead apportionment, allocation and absorption.
See Figure 1.1.
Alternative Investment Market (AIM)
Securities market designed primarily for small companies, regulated by the UK stock exchange but with less demanding rules than apply to the stock exchange official list of companies.
amortisation
Systematic allocation of the depreciable amount of an asset over its useful life (IAS 36). Normally applied to intangible assets and goodwill.
amortised cost (for a financial asset or liability)
Amount at which the financial asset or liability is measured, at initial recognition minus principal repayments, plus or minus cumulative amortisation using the effective interest in the item (refer to IAS 39).
analytical review
An audit technique used to help analyse data to identify trends, errors, fraud, inefficiency and inconsistency. Its purpose is to understand what has happened in a system, to compare this with a standard and to identify weaknesses in practice or unusual situations that may require further investigation. The main methods of analytical review are ratio analysis, non-financial performance analysis, internal and external benchmarking and trend analysis. While the purpose of analytical review in external audit is to understand financial performance and position and to identify areas for more in-depth audit treatment, analytical review in internal audit aims to better understand the control environment and identify potential control weaknesses.
annual equivalent rate (AER)
Notional annual rate which is equivalent to another set of rates that may be paid other than annually.
annual report and accounts
Package of information including a management report, an auditor's report and a set of financial statements with supportive notes. In the case of companies these are drawn up for a period which is called the accounting reference period, the last day of which is known as the reporting date.
annuity
Fixed periodic payment which continues either for a specified time, or until the occurrence of a specified event.
See perpetuity.
anti-dilution
Increase in earnings per share, or a reduction in loss per share, resulting from the assumption that convertible instruments are converted or options or warrants are exercised (refer to IAS 33).
Also see dilution.
apportion
To spread indirect revenues or costs over two or more cost units, centres, accounts or time periods. This may also be referred to as 'indirect allocation'.
re-apportion: The re-spread of costs apportioned to service departments to production departments.
See Figure 1.1 
apportionment basis
Physical or financial unit used to apportion costs to cost centres.
appropriation account
Record of how the surplus/deficit of a period has been allocated to distributions to owners and retentions by the entity.
arbitrage
Simultaneous purchase and sale of a security in different markets with the aim of making a risk-free profit through the exploitation of any price difference between the markets.
arrangement fees
See issue costs.
articles of association
Document which, with the memorandum of association, provides the legal constitution of a company. The articles of association define the rules and regulations governing the management of the affairs of the company, the rights of the members (shareholders), and the duties and powers of the directors.
See memorandum of association.
asset
Resource controlled by the entity as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity (IAS 38).
associate
An entity, including an unincorporated entity such as a partnership, over which the investor has significant influence and that is neither a subsidiary nor an interest in a joint venture (refer to IAS 28).
audit
Systematic examination of the activities and status of an entity, based primarily on investigation and analysis of its systems, controls and records.
audit, compliance
Audit of specific activities in order to determine whether performance is in conformity with a predetermined contractual, regulatory or statutory requirement.
audit, cost
Verification of cost records and accounts, and a check on adherence to prescribed cost accounting procedures and their continuing relevance.
audit, environmental
Systematic, documented, periodic and objective evaluation of how well an entity, its management and equipment are performing with the aim of helping to safeguard the environment by facilitating management control of environmental practices and assessing compliance with entity policies and external regulations.
audit, internal
Independent appraisal function established within an organisation to examine and evaluate its activities as a service to the organisation. The objective of internal auditing is to assist members of the organisation in the effective discharge of their responsibilities. To this end, internal auditing furnishes them with analyses, appraisals, recommendations, counsel and information concerning the activities reviewed (Institute of Internal Auditors—UK).
audit, management
Objective and independent appraisal of the effectiveness of managers and the corporate structure in the achievement of entity objectives and policies. Its aim is to identify existing and potential management weaknesses and to recommend ways to rectify them.
audit, post-completion
Objective, independent assessment of the success of a capital project in relation to plan. Covers the whole life of the project and provides feedback to managers to aid the implementation and control of future projects.
audit report
Formal document in which an auditor expresses an opinion as to whether the financial statements of an entity show a true and fair view of its position at a given date and the results of its operations for the accounting period ended on that date have been properly prepared in accordance with the relevant statutory requirements, accounting standards, or any report by an auditor in accordance with the terms of appointment.
audit, statutory external
Periodic examination of the books of accounts and records of an entity carried out by an independent third party (the auditor) to ensure that they have been properly maintained, are accurate and comply with established concepts, principles, accounting standards, legal requirements and give a true and fair view of the financial state of the entity.
audit trail
Linked chain of evidence which connects accounting information with the source document which verifies its validity.
audit, value for money
Investigation into whether proper arrangements have been made for securing economy, efficiency and effectiveness in the use of resources.
Auditing Practices Board (APB)
A body formed by an agreement between the six members of the Consultative Committee of Accountancy Bodies (CCAB), to be responsible for developing and issuing professional standards for auditors in the UK and the Republic of Ireland. From 2005, the APB will no longer issue its own standards but require the adoption of International Standards of Auditing (ISAs) issued by the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB).
See Consultative Committee of Accountancy Bodies.
available-for-sale financial assets
Non-derivative financial asset that is designated as being available for sale and not classified as loans and receivables, held-to-maturity investments, or financial assets held at fair value (IAS 39).
back-to-back loan
Form of financing whereby money borrowed in one country, or currency is covered by lending an equivalent amount in another.
BACS
Formerly the Bankers Automated Clearing Services. UK electronic bulk clearing system generally used by banks and building societies for low-value and/or repetitive items such as standing orders, direct debits and automated credits such as salary payments.
bad debt
Debt or trade receivable which is, or is considered to be, uncollectable and is, therefore, written off either as a charge to the income statement or against an existing doubtful debt provision.
See doubtful debts provision.
balance (on an account)
Difference between the totals of the debit and credit entries in an account.
balanced scorecard approach
Approach to the provision of information to the management to assist strategic policy formulation and achievement. It emphasises the need to provide the user with a set of information which addresses all relevant areas of performance in an objective and unbiased fashion. The information provided may include both financial and non-financial elements, and cover areas such as profitability, customer satisfaction, internal efficiency and innovation.
balance sheet
Statement of the financial position of an entity at a given date disclosing the assets, liabilities and equity (such as shareholders' contributions and reserves) prepared to give a true and fair view of the entity at that date.
See Figure 3.2.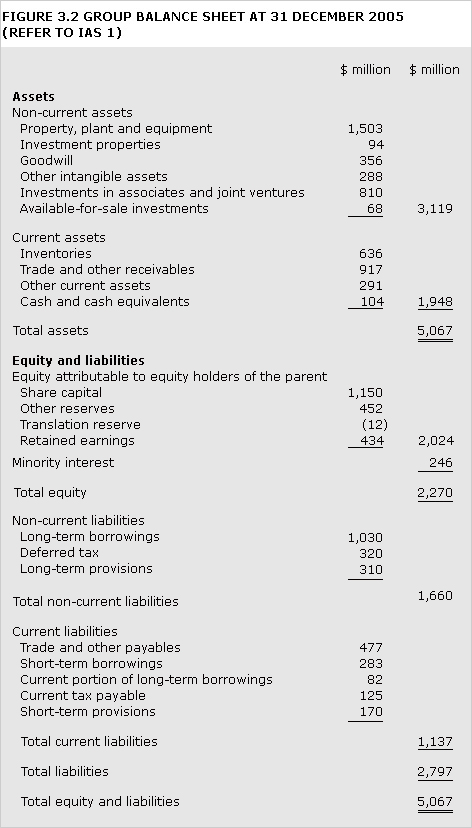
balancing allowance/charge
Relief for tax purposes of capital expenditure, or the claw back of relief already given, administered in the year in which a real asset is disposed of or an entity ceases to exist.
bank charge
Amount charged by a bank to its customers for services provided, for example for servicing customer accounts or arranging foreign currency transactions or letters of credit, but excluding interest.
bank overdraft
Borrowings from a bank on current account, normally repayable on demand. The maximum permissible overdraft is normally agreed with the bank prior to the facility being made available, and interest, calculated on a daily basis, is charged on the amount borrowed, and not on the agreed maximum borrowing facility.
bank reconciliation
Detailed statement reconciling, at a given date, the cash balance in an entity's cash book with that reported in a bank statement. An example is given below:
bankruptcy
Legal status of an individual against whom an adjudication order has been made by the court primarily because of inability to meet financial liabilities.
barrier to entry
Any impediment to the free entry of new competitors into a market.
barrier to exit
Any impediment to the exit of existing competitors from a market.
batch
Group of similar units which maintains its identity throughout one or more stages of production and is treated as a cost unit.
behavioural implications, accounting
Ways in which people affect, and are affected by, the creation, existence and use of accounting information. For example,
See budgeting, behavioural aspects and consequences.
bear market
Securities market experiencing a prolonged widespread decline in prices.
See bull market.
bearer bond
Negotiable bond (or security) whose ownership is not registered by the issuer, but is presumed to lie with whoever has physical possession of the bond.
benchmarking
Establishment, through data gathering, of targets and comparators that permit relative levels of performance (and particularly areas of underperformance) to be identified. Adoption of identified best practices should improve performance.
internal benchmarking: Comparing one operating unit or function with another within the same industry.
functional benchmarking: Comparing internal functions with those of the best external practitioners, regardless of their industry (also known as operational benchmarking or generic benchmarking).
competitive benchmarking: In which information is gathered about direct competitors through techniques such as reverse engineering.
strategic benchmarking: Type of competitive benchmarking aimed at strategic action and organisational change.
beta factor
Measure of systematic risk of a security relative to the market portfolio. If a security were to rise or fall at double the market rate, it would have a beta factor of 2.0. Conversely, if the security price moved at half the market rate, the beta factor would be 0.5.
See risk, market/systematic.
bid-ask spread
Difference between the buying and selling prices of a traded commodity or a financial instrument. Also known as bid-offer spread.
bill of lading
Document prepared by a consignor by which a carrier acknowledges the receipt of goods and which serves as a document of title to the goods consigned.
bill of materials
Detailed specification, for each product, of the subassemblies, components and materials required, distinguishing items purchased externally from those manufactured in-house.
bill payable
Bill of exchange or promissory note payable.
bill receivable
Bill of exchange or promissory note receivable.
Black-Scholes method (share options)
Equation developed by F. Black and M. Scholes to value a European-style call option that uses the share price, the exercise price, the risk-free interest rate, the time to maturity and the standard deviation of the share return. A European option can be exercised only on the expiration date.
See European-style option (option).
blue chip
Description of an equity or company which is of the highest quality, and in which an investment would be regarded as low risk with regard to both dividend payments and capital values.
bond
Debt instrument, normally offering a fixed rate of interest (coupon) over a fixed period of time, and with a fixed redemption value (par).
bonus/scrip issue
Capitalisation of the reserves of an entity by the issue of additional shares to existing shareholders in proportion to their holdings. Such shares are normally fully paid-up with no cash called for from the shareholders.
See rights issue.
bookkeeping
Recording of monetary transactions, appropriately classified, in the financial records of an entity.
See double entry bookkeeping.
borrowing costs
Interest and other costs incurred by an entity in connection with the borrowing of funds. They may include:
(a) interest on bank overdrafts and borrowings;
(b) amortisation of discounts or premiums related to borrowings;
(c) amortisation of ancillary costs incurred in connection with the arrangement of borrowings;
(d) finance charges in respect to finance leases; and
(e) exchange differences arising from foreign currency borrowings to the extent they are regarded as an adjustment to interest costs (IAS 23).
Boston Consulting Group matrix
A representation of an entity's product or service offerings which shows the value of each product's sales expressed in relation to the growth rate of the market served and the market share held. The objective of the matrix is to assist in the allocation of funds to products. Products can be classified as star, cash cow, problem child or dog, according to their position on the matrix.
See Figure 2.1.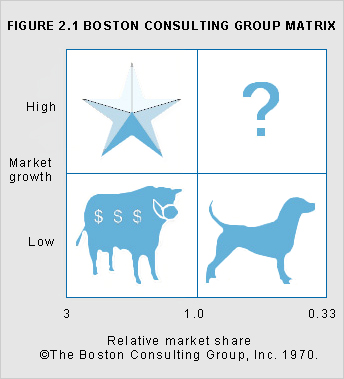
bottleneck
Facility that has lower capacity than prior or subsequent facilities and restricts output based on current capacity.
See theory of constraints, throughput.
breakeven chart
Chart that indicates approximate profit or loss at different levels of sales volume within a limited range. For examples of conventional breakeven charts under different cost structures,
See Figures 1.3 and 1.4. Figure 1.5 shows a contribution breakeven chart and Figure 1.6 a profit-volume chart.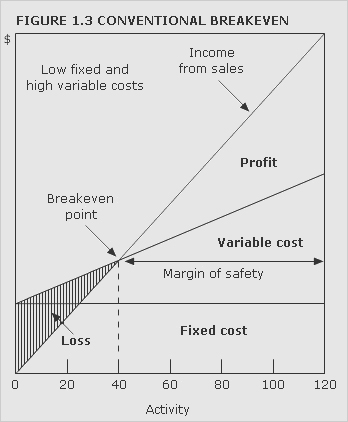
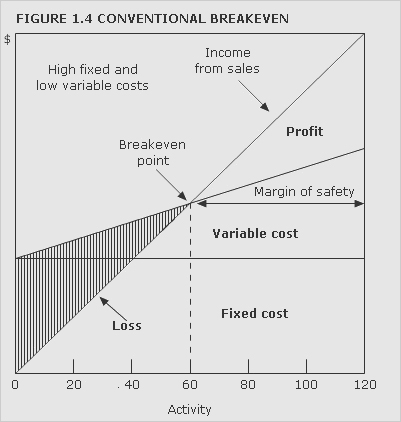
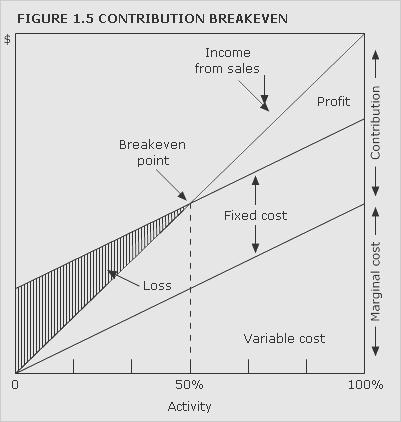
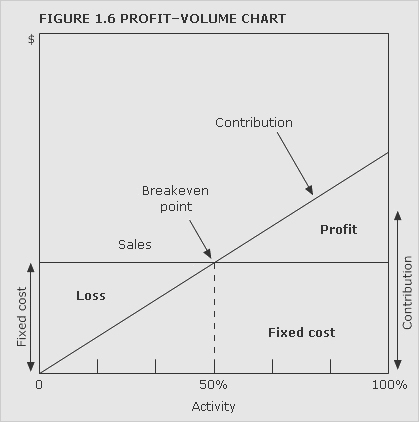
breakeven point
Level of activity at which there is neither profit nor loss. It can be ascertained by using a breakeven chart or by calculation.
See Figures 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6 and example: 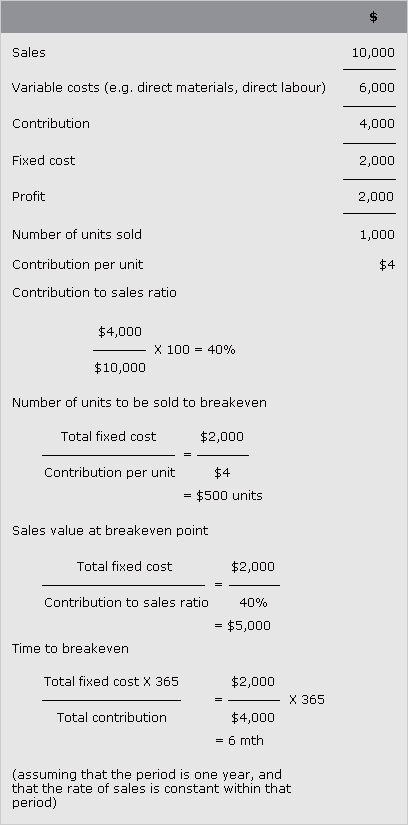
budget
Quantitative expression of a plan for a defined period of time. It may include planned sales volumes and revenues; resource quantities, costs and expenses; assets, liabilities and cash flows.
budget, cash
Detailed budget of estimated cash inflows and outflows incorporating both revenue and capital items.
budget centre
Section of an entity for which control may be exercised through prepared budgets. It is often a responsibility centre where the manager has authority over, and responsibility for, defined costs and (possibly) revenues.
budget cost allowance
Calculated after an accounting period, the cost allowance reflects the actual level of output achieved. Variable costs are flexed in proportion to volume achieved and fixed costs are based on the annual budget.
budget, departmental/functional
Budget of income and/or expenditure applicable to a particular function frequently including sales budget, production cost budget (based on budget production, efficiency and utilisation), purchasing budget, human resources budget, marketing budget, and research and development budget.
budget, fixed
Budget set prior to the control period and not subsequently changed in response to changes in activity, costs or revenues. It may serve as a benchmark in performance evaluation.
budget, flexible
See budget flexing.
budget flexing
Flexing variable costs from original budgeted levels to the allowances permitted for actual volume achieved while maintaining fixed costs at original budget levels. (Variable cost allowance = Ratio of actual volume achieved to budget volume x original budget variable cost)
budget lapsing
Withdrawal of unspent budget allowance due to the expiry of the budget period.
budget, line item
Traditional form of budget layout showing, line by line, the costs of a cost centre analysed by their nature (for example salaries, occupancy, maintenance).
budget manual
Detailed set of guidelines and information about the budget process typically including a calendar of budgetary events, specimen budget forms, a statement of budgetary objectives and desired results, listing of budgetary activities and budget assumptions regarding, for example, inflation and interest rates.
budget, master
Consolidates all subsidiary budgets and is normally comprised of the budgeted profit and loss account, balance sheet and cash flow statement.
budget, operating
Budget of the revenues and expenses expected in a forthcoming accounting period.
budget padding
See budget slack
budget period
Period for which a budget is prepared and used, which may then be subdivided into control periods.
budget, principal factor
Principal budget factor limits the activities of an undertaking. Identification of the principal budget factor is often the starting point in the budget setting process. Often the principal budget factor will be sales demand but it could be production capacity or material supply.
budget purposes
Budgets may help in authorising expenditure, communicating objectives and plans, controlling operations, co-ordinating activities, evaluating performance, planning and rewarding performance. Often, reward systems involve comparison of actual with budgeted performance.
budget, rolling/continuous
Budget continuously updated by adding a further accounting period (month or quarter) when the earliest accounting period has expired. Its use is particularly beneficial where future costs and/or activities cannot be forecast accurately.
See rolling forecast.
budget setting processes
bottom-up budgeting: Budgeting process where all budget holders have the opportunity to participate in setting their own budgets.
imposed/top-down budgeting: Budgeting process where budget allowances are set without permitting ultimate budget holders the opportunity to participate in the process.
negotiated budget: Budget in which budget allowances are set largely on the basis of negotiations between budget holders and those to whom they report.
participative budgeting:
See bottom-up budgeting.
budget slack
Intentional overestimation of expenses and/or underestimation of revenue during budget setting. Also known as budget padding.
budget virement
Authority to apply saving under one budget subhead to meet excesses on others.
budgetary control
Master budget, devolved to responsibility centres, allows continuous monitoring of actual results versus budget, either to secure by individual action the budget objectives or to provide a basis for budget revision.
See control, feedback and control, feedforward.
budgeting, behavioural aspects and consequences
budget constrained style: Excessive pressure to achieve budgets that can lead to job-related tension, recriminations, buck—passing and budget padding.
non-accounting style: Management style that largely ignores budgets and financial information.
profit conscious style: Management style that takes account of budgets together with other information and evaluates managerial performance in a flexible manner.
target setting: 'Tight but achievable' levels are recommended to motivate optimum performance. Too loose a budget can lead to under-achievement as can too tight a budget—and this can also be de-motivating.
budgeting, beyond
Idea that companies need to move beyond budgeting because of the inherent flaws in budgeting especially when used to set incentive contracts. It is argued that a range of techniques, such as rolling forecasts and market-related targets, can take the place of traditional budgets.
budgeting, incremental
Method of budgeting based on the previous budget or actual results, adjusting for known changes and inflation, for example.
budgeting, priority-based
Method of budgeting whereby budget requests are accompanied by a statement outlining the changes expected if the prior period budget were increased or decreased by a certain amount or percentage. These changes are prioritised.
budgeting, zero-based
Method of budgeting that requires all costs to be specifically justified by the benefits expected.
bull market
Securities market experiencing prolonged widespread price increases.
See bear market.
burden
US equivalent of 'overhead'.
business angels
Wealthy individuals prepared to invest in a start-up, early stage or developing firm. Often, they have managerial and/or technical experience to offer to the management team as well as debt and equity finance.
business combination
Bringing together of separate entities or businesses into one reporting entity (IFRS 3). In all business combinations, one entity (the acquirer) will obtain control of another entity (the acquiree) and an acquirer should be identified for all such combinations. (This means all business combinations involving an acquirer and an acquiree should be accounted for by applying the purchase (acquisition) method. The 'uniting of interests' (merger) method is now abolished.) Refer to IFRS 3.
business process re-engineering
Selection of areas of business activity in which repeatable and repeated sets of activities are undertaken, and the development of improved understanding of how they operate and of the scope for radical redesign with a view to creating and delivering better customer value.
business segment
Distinguishable component of an entity that is engaged in providing an individual product or service (or group of products or services) and that is subject to risks and returns that are different from those of other segments (IAS 14).
See geographic segment.
by-product
Output of some value produced incidentally while manufacturing the main product.
See joint products.
call
Request made to the holders of partly paid-up share capital for the payment of a predetermined sum due on the share capital, under the terms of the original subscription agreement. Failure on the part of the shareholder to pay a call may result in the forfeiture of the relevant holding of partly paid shares.
call off
System whereby stock is held at the customer's premises, to be invoiced only on use.
call option
Option to buy a specified underlying asset at a specified exercise price on, or before, a specified exercise date.
See exercise price, option, put option.
capital allowance
Relief from income tax or corporation tax on capital expenditure on eligible assets.
capital asset pricing model (CAPM)
Theory which predicts that the expected risk premium for an individual stock will be proportional to its beta, such that: (Expected risk premium on a stock = beta x expected risk premium in the market.) Risk premium is defined as the expected incremental return for making a risky investment rather than a safe one.
capital budgeting
Process concerned with decision-making in respect of the choice of specific investment projects and the total amount of capital expenditure to commit.
capital employed
Investment in an entity. In assessing managers it is usually calculated as total assets less current liabilities.
equity capital employed: Shareholders' stake in the company. This is important when calculating return to shareholders.
capital expenditure
Costs incurred in acquiring, producing or enhancing non-current assets (both tangible and intangible).
See revenue expenditure.
capital expenditure control
Procedures for authorising and subsequently monitoring capital expenditure.
capital expenditure proposal/authorisation
Formal request for authority to incur capital expenditure usually supported by the case for expenditure in accordance with capital investment appraisal criteria. Levels of authority should be clearly defined with reporting of actual expenditure to the equivalent authority levels.
capital gain/loss
Extent by which the net realised value of a capital asset exceeds (or in the case of a capital loss is less than) the cost of acquisition plus additional improvements, less depreciation charges where applicable. It can also arise from the exchange of such an asset for another of a different type. The term can have other interpretations for tax purposes.
capital instrument
All instruments that are issued by reporting entities as a means of raising finance, including shares, debentures, loans and debt instruments, options and warrants that give the holder the right to subscribe for or obtain capital instruments. In the case of consolidated financial statements the term includes capital instruments issued by subsidiaries except those that are held by another member of the group included in the consolidation (FRS 4).
capital investment appraisal
Application of a set of methodologies (generally based on the discounting of projected cash flows) whose purpose is to give guidance to managers with respect to decisions as to how best to commit long-term investment funds.
See discounted cash flow.
capital maintenance
Principle that profit is only recorded after capital has been maintained intact. There are two bases on which capital can be defined, financial and physical.
capital rationing
Restriction on an entity's ability to invest capital funds, caused by an internal budget ceiling being imposed on such expenditure by management (soft capital rationing), or by external limitations being applied to the company, as when additional borrowed funds cannot be obtained (hard capital rationing).
capital redemption reserve
Account required to prevent a reduction in capital, where an entity purchases or redeems its own shares out of distributable profits.
capital structure
Relative proportions of equity capital and debt capital within an entity's balance sheet.
capital surplus
Assets remaining in an entity after all costs and liabilities have been discharged. It is distributed amongst the shareholders in accordance with the rights as determined at the time of the issue of shares.
capitalisation
Recognising a cost as part of the cost of an asset (IAS 23). The asset will be included in the balance sheet as a non-current asset.
carrying amount
Amount at which an asset is recognised in the balance sheet after deducting any accumulated depreciation (or amortisation) and accumulated impairment losses thereon (IAS 36).
cash
Cash on hand and demand deposits (IAS 7).
cash cow
Product characterised by a high market share but low market growth, whose function is seen as generating cash for use elsewhere within the entity.
cash equivalents
Short-term, highly liquid investments that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash and which are subject to insignificant risk of changes in value (IAS 7).
cash flow statement
Summarises the inflows and outflows of cash (and cash equivalents) for a period, classified under the following headings: operating activities, investing activities and financing activities (refer to IAS 7).
See Figure 3.3.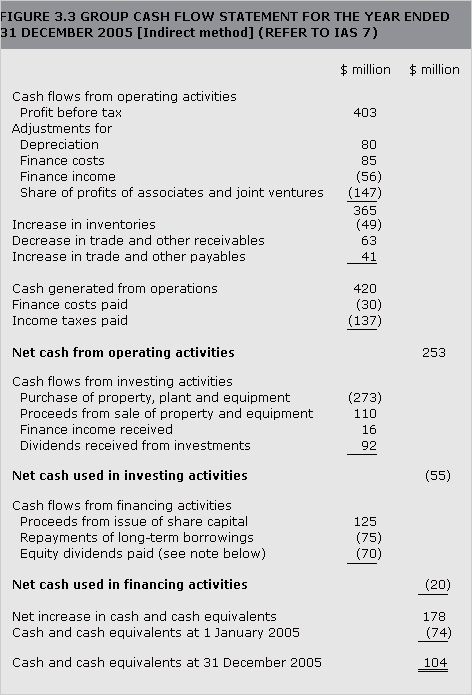
cash generating unit
Smallest identifiable group of assets that generates cash inflows that are largely independent of the cash inflows from other assets or groups of assets (IAS 36).
cash management models
Sophisticated cash flow forecasting models which assist management in determining how to balance the cash needs of an entity. Cash management models can help: to optimise cash balances; to manage customer, supplier, investor and company needs; to determine whether to invest or buy back shares; and to decide what is the optimum of financing working capital.
centre
Department, area or function to which costs and/or revenues are charged.
See Figure 1.1.
budget centre: Centre for which an individual budget is drawn up.
cost centre: Production or service location, function, activity or item of equipment for which costs are accumulated.
See Figure 1.1.
investment centre: Profit centre with additional responsibilities for capital investment and possibly for financing, and whose performance is measured by its return on investment.
profit centre: Part of a business accountable for both costs and revenues.
responsibility centre: Departmental or organisational function whose performance is the direct responsibility of a specific manager.
revenue centre: Centre devoted to raising revenue with no responsibility for costs, for example a sales centre. Often used in not-for-profit organisations.
service cost centre: Cost centre providing services to other cost centres. When the output of an organisation is a service, rather than goods, an alternative name is normally used, for example support cost centre or utility cost centre.
See Figure 1.1
certainty equivalent method
Approach to dealing with risk in a capital budgeting context. It involves expressing risky future cash flows in terms of the certain cash flow which would be considered, by the decision maker, as their equivalent, that is the decision maker would be indifferent between the risky amount and the (lower) riskless amount considered to be its equivalent.
certificate of deposit
Negotiable instrument which provides evidence of a fixed-term deposit with a bank. Maturity is normally within 90 days, but can be longer.
CHAPS
Clearing House Automated Payment System. UK method for the rapid electronic transfer of funds between participating banks on behalf of large commercial customers, where transfers tend to be of significant value.
chartered entity
Organisation formed by the grant of a Royal Charter (in the UK). The charter authorises the entity to operate and states the powers specifically granted.
chart of accounts
Comprehensive and systematically arranged list of the named and numbered accounts applicable to an entity.
See Figure 3.4.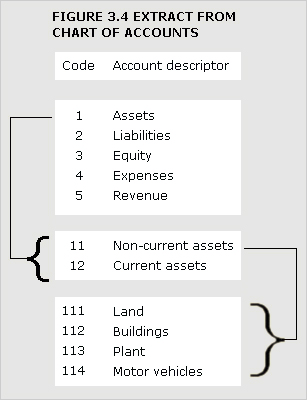
classification
Arrangement of items in logical groups by nature, purpose or responsibility. Classification systems allow financial information to be reported under subjective headings, by cost object or responsibility centre.
See code.
closing rate
Spot exchange rate (a rate for immediate delivery) at the balance sheet date (IAS 21).
code
Brief, accurate reference designed to assist classification of items by facilitating entry, collation and analysis. For example, in costing, the first three digits in the composite symbol 211.392 might indicate the nature of the expenditure (subjective classification), and the last three digits might indicate the cost centre or cost unit to be charged (objective classification).
code of ethics
Set of standards governing the conduct of members of a certain profession, by specifying expected standards for competence, professional behaviour and integrity. All members of the International Federation Accountants (IFAC) are expected to model their ethical codes on the IFAC code. There is therefore a specific ethical code for CIMA members.
collateral
Security, in the form of a claim over assets, generally given for borrowed funds over the period of a loan.
commercial paper
Unsecured short-term loan notes issued by companies, and generally maturing within a period of up to one year.
commitment accounting
Method of accounting which recognises expenditure as soon as it is contracted.
committee, audit
Formally constituted committee of an entity's main board of directors whose responsibilities include: monitoring the integrity of any formal announcements on financial performance including financial statements; reviewing internal financial controls, internal control and risk management systems; monitoring the effectiveness of the internal audit function; making recommendations in respect of the appointment or removal of the external auditor; reviewing and monitoring auditor independence and the effectiveness of the audit process.
committee, nominations
Formally constituted committee of an entity's main board of directors. The committee's main functions are to establish the criteria for board membership, identify suitable candidates and make recommendations for appointment to the board.
committee, remuneration
Formally constituted committee of an entity's main board of directors whose primary function is to consider the performance and remuneration of the executive directors. Remuneration issues will include performance-related payments, pension rights, compensation payments and share option schemes.
commodity pricing
Pricing a product or service on the basis that it is undifferentiated from all competitive offerings, and cannot therefore command any price premium above the base market price.
company limited by guarantee
Company in which each member undertakes to contribute (to the limit of the guarantee), on a winding up, towards payment of the liabilities of the company.
company limited by shares/joint stock company/limited liability company
Company in which the liability of members for the company's debts is limited to the value of the shares taken up by them.
See private company and public company.
company/corporation
Legal entity, whose life is independent of that of its members. In the UK, companies or corporations are predominantly formed through registration under the UK Companies Act 1985.
competitive advantage
Situation where an organisation exerts more competitive force on its competitors than they exert on it.
See Porter's five forces
competitive forces
See Porter's five forces
competitor analysis
Identification and quantification of the relative strengths and weaknesses (compared with competitors or potential competitors), which could be of significance in the development of a successful competitive strategy.
component of an entity
Operations and cash flows that can be clearly distinguished operationally, and for financial reporting purposes, from the rest of the entity (IFRS 5).
compound instrument
Financial instrument that, from the issuer's perspective, contains both a liability and an equity element (IAS 32).
compound interest
Interest which is calculated over successive periods based on the principal plus accrued interest.
See simple interest.
The future value of an investment, over whose period interest is compounded, can be found by using the following formula:
conglomerate
Entity comprising a number of dissimilar businesses.
consignment inventory
Inventory held by one party (the dealer) but legally owned by another (the manufacturer) on terms that may give the dealer the right to sell the inventory in the normal course of business or, at the dealer's option, return it unsold to the manufacturer.
consol
Certain irredeemable UK government stocks carrying fixed coupons. Sometimes used as a general term for an undated or irredeemable bond.
consolidated financial statements
Financial statements of a group presented as those of a single economic entity (IAS 27).
consortium
Association of several entities with a view to carrying out a joint venture.
See joint venture
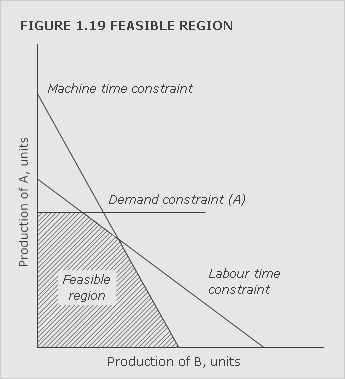
constraint
Activity, resource or policy that limits the ability to achieve an objective.
See theory of constraints.
In linear programming, constraints define the feasible region within which a solution must lie.
See linear programming.
See Figure 1.19.
construction contract
Specifically negotiated for the construction of an asset or a combination of assets that are closely inter-related or inter-dependent in terms of their design, technology and function or their ultimate purpose or use (IAS 11).
constructive obligation
Obligation that derives from an entity's actions where: (a) by an established pattern of past practice, published policies or a sufficiently specific current statement, the entity has indicated to other parties that it will accept certain responsibilities; and (b) as a result, the entity has created a valid expectation on the part of those other parties that it will discharge those responsibilities (IAS 37).
Consultative Committee of Accountancy Bodies (CCAB)
A forum (now a limited company) in which matters affecting the six member bodies and the UK and Irish professions as a whole can be discussed and co-ordinated, thus allowing the profession to speak with a unified voice to the UK and Irish governments. The six member bodies are ACCA, CIMA, CIPFA, ICAEW, ICAI and ICAS.
contingency plan
A plan, formulated in advance, to be implemented upon the occurrence of certain specific future events.
contingent asset
Possible asset that arises from past events and whose existence will be confirmed only by the occurrence of one or more uncertain future events not wholly within the control of the entity (IAS 37).
contingent liability
(a) A possible obligation that arises from past events and whose existence will be confirmed only by the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more uncertain future events not wholly within the entity's control; or (b) A present obligation that arises from past events but is not recognised because it is not probable that a transfer of economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation; or the amount of the obligation cannot be measured with sufficient reliability (IAS 37).
continuing operation
See discontinued operation.
continuous improvement
Derived from the Japanese term kaizen. A simple idea but when taken seriously over a period can lead to significant improvements.
See kaizen.
contribution
(sales value – variable cost of sales)
Contribution may be expressed as total contribution, contribution per unit or as a percentage of sales.
See Figure 1.7.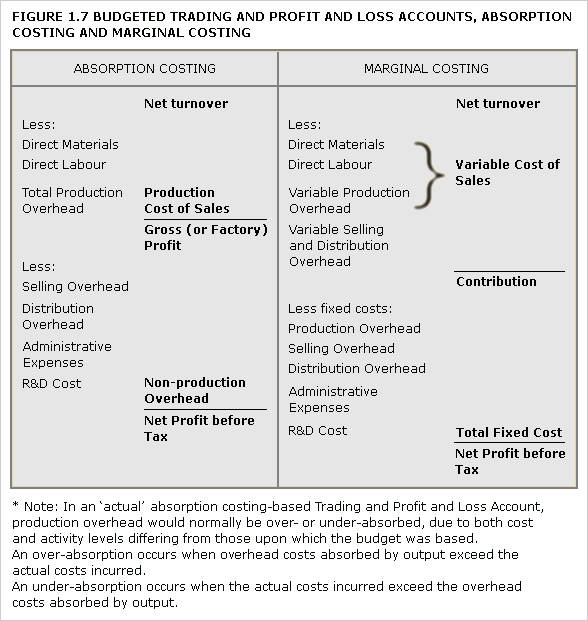
control
In management accounting, control usually means ensuring that activities planned and undertaken lead to desired outcomes.
See control, feedback and control, feedforward.
control (in the context of an asset)
Ability to obtain the future economic benefits relating to an asset and to restrict the access of others to these benefits.
control (of an entity)
Power to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity so as to obtain benefits from its activities (IAS 27).
control, feedback
Measurement of differences between planned outputs and actual outputs achieved, and the modification of subsequent action and/or plans to achieve future required results. Feedback control is an integral part of budgetary control and standard costing systems.
See Figure 1.8.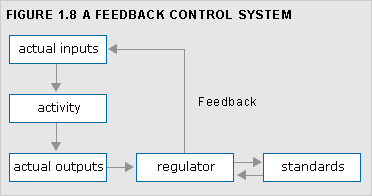
control, feedforward
Forecasting of differences between actual and planned outcomes, and the implementation of action, before the event, to avoid such differences.
See Figure 1.9.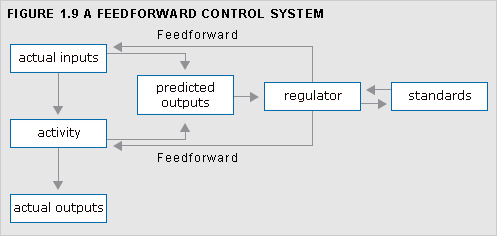
control, management
All of the processes used by managers to ensure that organisational goals are achieved and procedures adhered to, and that the organisation responds appropriately to changes in its environment.
closed loop system: Control system that includes provision for corrective action, taken on either a feedforward or a feedback basis.
See Figures 1.8 and 1.9.


open loop system : Control system that includes no provision for corrective action to be applied to the sequence of activities.
control, operational
Management of daily activities in accordance with strategic and tactical plans.
See Figure 1.10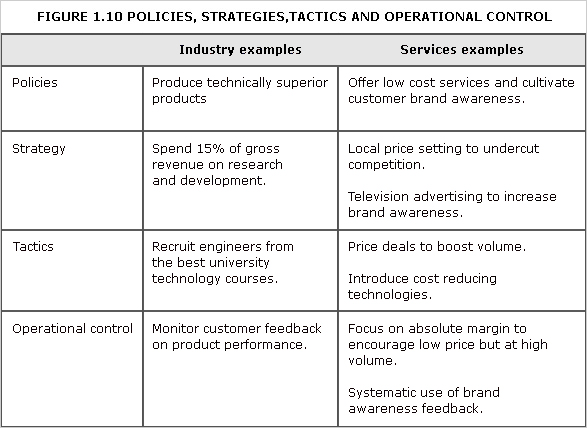
convertible debt
Liability that gives the holder the right to convert into another instrument, normally ordinary shares at a predetermined price/rate and time.
corporate appraisal
Critical assessment of the strengths and weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT analysis) in relation to the internal and environmental factors affecting an entity in order to establish its condition prior to the preparation of the long-term plan.
corporate social accounting
Reporting of the social and environmental impact of an entity's activities upon those who are directly associated with the entity (for instance, employees, customers, suppliers) or those who are in any way affected by the activities of the entity, as well as an assessment of the cost of compliance with relevant regulations in this area.
corporation tax
Tax chargeable on companies resident in the UK or trading in the UK. Referred to internationally as income tax.
cost
As a noun: the amount of cash or cash equivalent paid or the fair value of other consideration given to acquire an asset at the time of its acquisition or construction (IAS 16). As a verb: to ascertain the cost of a specified thing or activity. The word cost can rarely stand alone and should be qualified as to its nature and limitations.
cost account
Record of expenditure associated with a cost object such as a job, batch, contract or process. Revenue may be credited to the account as, for example, when a process by-product has value.
cost accounting
Gathering of cost information and its attachment to cost objects, the establishment of budgets, standard costs and actual costs of operations, processes, activities or products; and the analysis of variances, profitability or the social use of funds. The use of the term costing is not recommended except with a qualifying adjective, for example: standard costing, batch costing, continuous operation costing, contract costing, job costing, service/fn costing, specific order costing and marginal costing.
cost accounting—for cost objects
batch costing: Form of specific order costing where costs are attributed to batches of product (unit costs can be calculated by dividing by the number of products in the batch).
See figure 1.11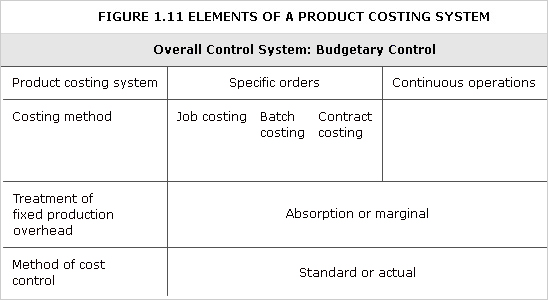
contract costing: Form of specific order costing where costs are attributed to contracts.
See Figure 1.11.
job costing: Form of specific order costing where costs are attributed to individual jobs.
See Figure 1.11. 
operations costing: Form of costing where costs are attributed to individual operations within a manufacturing process.
process costing: Form of costing applicable to continuous processes where process costs are attributed to the number of units produced. This may involve estimating the number of equivalent units in stock at the start and end of the period under consideration.
See Figure 1.11. 
specific order costing: Basic cost accounting method applicable if work consists of separately identifiable batches, contracts or jobs.
See Figure 1.11.
cost accounting—methods
absorption costing: Assigns direct costs and all or part of overhead to cost units using one or more overhead absorption rates.
See Figure 1.1.
Sometimes referred to as full costing although this is a misnomer if all costs are not attributed to cost units.
direct costing: See variable costing.
full costing: See absorption costing.
marginal costing: See variable costing.
uniform costing: Used by several undertakings, usually in the same industry, of the same costing methods, principles and techniques.
variable costing: Assigns only variable costs to cost units while fixed costs are written off as period costs.
See Figure 1.7.
Also known as marginal costing and, especially in the US, as direct costing.
cost allocation/apportionment
See allocation and apportionment.
cost, avoidable
Specific cost of an activity or sector of a business that would be avoided if the activity or sector did not exist.
cost behaviour
Variability of input costs with activity undertaken. Cost may increase proportionately with increasing activity (the usual assumption for a variable cost), or it may not change with increased activity (a fixed cost). Some costs (semi-variable) may have both variable and fixed elements. Other behaviour is possible, costs may increase more or less than in direct proportion, and there may be step changes in cost, for example. To a large extent cost behaviour will be dependent on the timescale assumed.
See Figures 1.12 and 1.13.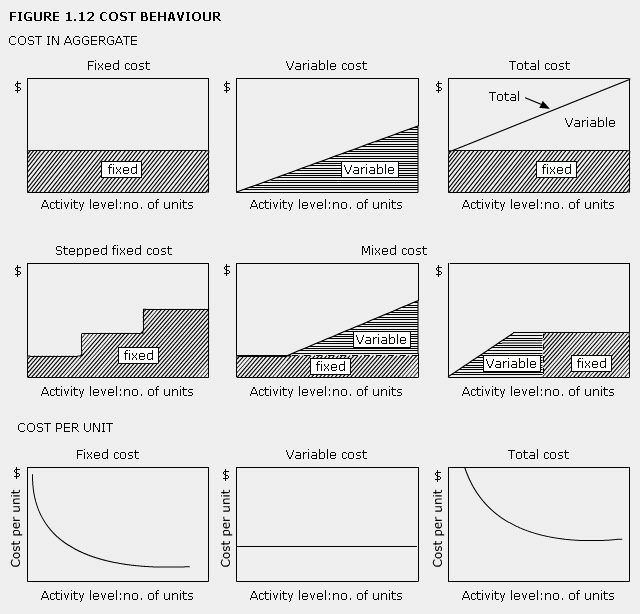
cost-benefit analysis
Comparison between the costs of the resources used plus any other costs imposed by an activity (for example pollution, environmental damage) and the value of the financial and non-financial benefits derived.
cost classification
Arrangement of elements of cost into logical groups with respect to their nature (fixed, variable, value adding), function (production, selling) or use in the business of the entity.
cost, committed
Cost arising from prior decisions, which cannot, in the short run, be changed. Committed cost incurrence often stems from strategic decisions concerning capacity with resulting expenditure on plant and facilities. Initial control of committed costs at the decision point is through investment appraisal techniques.
See commitment accounting.
See Figure 1.14.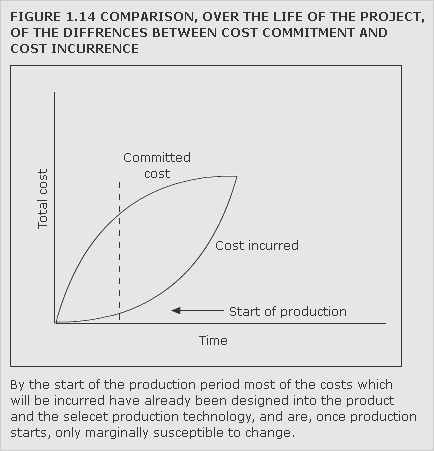
cost, common
Cost relating to more than one product or service.
cost, contract
Aggregated costs of a single contract. This usually applies to major long-term contracts rather than short-term jobs.
cost control
Process that ensures action is taken if costs exceed a pre-set allowance (See control, feedback) or that action is taken if costs are forecast to exceed expected levels.
See control, feedforward.
cost, controllable
Cost that can be controlled, typically by a cost, profit or investment centre manager.
cost, conversion
Cost of converting material into finished product, typically including direct labour, direct expense and production overhead.
cost, differential/incremental
Difference in total cost between alternatives. This is calculated to assist decision making.
cost, direct
Expenditure that can be attributed to a specific cost unit, for example material that forms part of the product.
See Figure 1.1.
cost, discretionary
Cost whose amount within a time period is determined by a decision taken by the appropriate budget holder. Marketing, research and training are generally regarded as discretionary costs. Also known as managed or policy costs.
cost driver
Factor influencing the level of cost. Often used in the context of ABC to denote the factor which links activity resource consumption to product outputs, for example the number of purchase orders would be a cost driver for procurement cost.
cost elements
Constituent parts of costs according to the factors upon which expenditure is incurred, namely material, labour and expenses.
See Figure 1.15.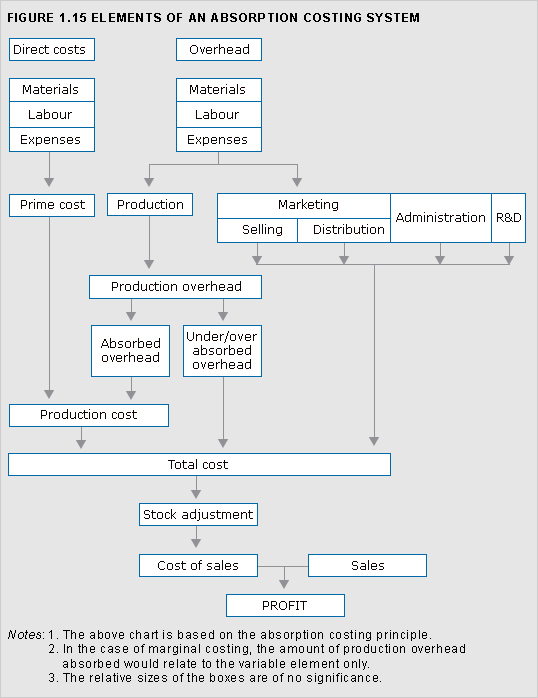
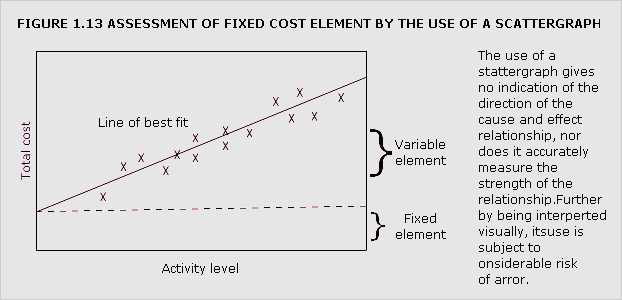
cost estimation
Determination of cost behaviour. This can be achieved by engineering methods, analysis of the accounts, use of statistics or by the pooling of expert views.
cost, fixed
Cost incurred for an accounting period, that, within certain output or turnover limits, tends to be unaffected by fluctuations in the levels of activity (output or turnover).
cost, holding
Cost of retaining an asset, generally stock. Holding cost includes the cost of financing the asset in addition to the cost of physical storage.
cost, joint
Cost of a process which results in more than one main product.
cost, long-term variable
All costs are variable in the long run. Full unit costs may be surrogates for long-term variable costs if calculated in a manner which utilises long-term cost drivers, for example activity-based costing.
cost management
Application of management accounting concepts, methods of data collection, analysis and presentation in order to provide the information needed to plan, monitor and control costs.
cost, marginal
Part of the cost of one unit of product or service that would be avoided if the unit were not produced, or that would increase if one extra unit were produced.
cost, notional
Cost used in product evaluation, decision making and performance measurement to reflect the use of resources that have no actual (observable) cost. For example, notional interest for internally generated funds or notional rent for use of space.
cost object
For example a product, service, centre, activity, customer or distribution channel in relation to which costs are ascertained.
cost of capital
Minimum acceptable return on an investment, generally computed as a discount rate for use in investment appraisal exercises. The computation of the optimal cost of capital can be complex, and many ways of determining this opportunity cost have been suggested.
See weighted average cost of capital
cost of quality
Difference between the actual cost of producing, selling and supporting products or services and the equivalent costs if there were no failures during production or usage. The cost of quality can be analysed into:
cost of conformance: Cost of achieving specified quality standards.
cost of prevention: Costs incurred prior to or during production in order to prevent substandard or defective products or services from being produced.
cost of appraisal: Costs incurred in order to ensure that outputs produced meet required quality standards.
cost of non-conformance: Cost of failure to deliver the required standard of quality.
cost of internal failure: Costs arising from inadequate quality which are identified before the transfer of ownership from supplier to purchaser.
cost of external failure: Cost arising from inadequate quality discovered after the transfer of ownership from supplier to purchaser.
Note: There is no universally accepted definition of quality, which may be assessed on a number of bases, such as conformance to specification, ability to satisfy wants, inclusion of attractive performance/aesthetic attributes, or offering value for money.
cost of sales
The cost of goods sold during an accounting period. For a retail business this will be the cost of goods available for sale (opening stock plus purchases) minus closing stock. For a manufacturing business it will include all direct and indirect production costs.
cost, opportunity
The value of the benefit sacrificed when one course of action is chosen in preference to an alternative. The opportunity cost is represented by the foregone potential benefit from the best rejected course of action.
cost, overhead/indirect
Expenditure on labour, materials or services that cannot be economically identified with a specific saleable cost unit. The synonymous term burden is in common use in the US and in subsidiaries of American companies.
cost, period
Cost relating to a time period rather than to the output of products or services.
cost pool
Grouping of costs relating to a particular activity in an activity-based costing system.
cost, post-purchase
Cost incurred after a capital expenditure decision has been implemented and facilities acquired. May include training, maintenance and the cost of upgrades.
cost, prime
Total cost of direct material, direct labour and direct expenses.
cost, product
Cost of a finished product built up from its cost elements.
cost, production
Prime cost plus absorbed production overhead.
cost, replacement
Cost of replacing an asset. This is important in relevant costing because if, for example, material that is in constant use is needed for a product or service, the relevant cost of that material will be its replacement cost. Replacement cost has also been proposed as an alternate to historic cost accounting and it can, therefore, be an important concept with relevance to accounting for inflation or measuring performance where the value of assets is important.
cost, semi-variable
Cost containing both fixed and variable components and thus partly affected by a change in the level of activity.
cost, standard
Planned unit cost of a product, component or service. The standard cost may be determined on a number of bases (see standard). The main uses of standard costs are in performance measurement, control, stock valuation and in the establishment of selling prices.
See standard product specification.
cost, sunk
Cost that has been irreversibly incurred or committed and cannot therefore be considered relevant to a decision. Sunk costs may also be termed irrecoverable costs.
cost table
Database containing costs associated with production of a product, broken down by function and/or components and sub-assemblies. It incorporates cost changes that would result from possible changes in the input mix.
cost, target
Product cost estimate derived by subtracting a desired profit margin from a competitive market price.
cost unit
Unit of product or service in relation to which costs are ascertained.
See Figure 1.16.
cost, variable
Cost that varies with a measure of activity.
cost-volume-profit analysis (CVP)
Study of the effects on future profit of changes in fixed cost, variable cost, sales price, quantity and mix.
cost, weighted average
Method of unit cost determination, often applied to stocks, in which an average unit cost is calculated, when a new purchase quantity is received: ![]()
See Figure 1.17.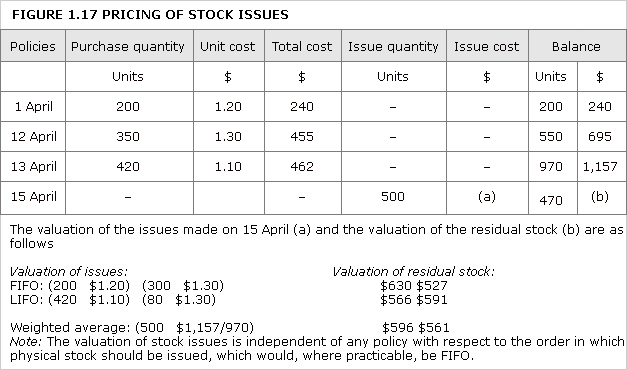
costing, backflush
Method of costing, associated with a JIT (just-in-time) production system, which applies cost to the output of a process. Costs do not mirror the flow of products through the production process, but are attached to output produced (finished goods stock and cost of sales), on the assumption that such backflushed costs are a realistic measure of the actual costs incurred.
See just-in-time.
costing, life-cycle
Maintenance of physical asset cost records over entire asset lives, so that decisions concerning the acquisition use or disposal of assets can be made in a way that achieves the optimum asset usage at the lowest possible cost to the entity. The term may be applied to the profiling of cost over a product's life, including the pre-production stage (terotechnology), and to both company and industry life cycles
See Figure 1.18.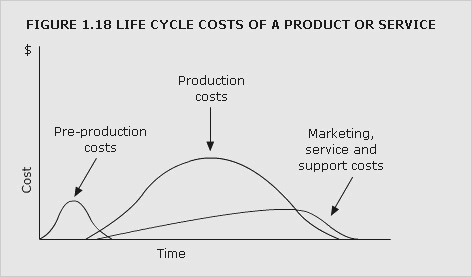
costing, standard
Control technique that reports variances by comparing actual costs to pre-set standards so facilitating action through management by exception.
countertrade
Form of trading activity based on other than an arm's-length goods for cash exchange. Types of countertrade include:
barter: Direct exchange of goods and services between two parties without the use of money.
counterpurchase: Trading agreement in which the primary contract vendor agrees to make purchases of an agreed percentage of the primary contract value, from the primary contract purchaser, through a linked counterpurchase contract.
Offsets: Trading agreement in which the purchaser becomes involved in the production process, often acquiring technology supplied by the vendor.
coupon
Interest payable on a bond expressed as a percentage of the nominal value.
creative accounting
Form of accounting which, while complying with all regulations and practices, nevertheless gives a biased impression (generally favourable) of an entity's financial performance and position.
See window-dressing.
creditor
See payables.
credit scoring
Assessment of the creditworthiness of an individual or company by rating numerically a number of both financial and non-financial aspects of the target's present position and previous performance.
critical success factor
An element of organisational activity which is central to its future success. Critical success factors may change over time, and may include items such as product quality, employee attitudes, manufacturing flexibility and brand awareness.
cum
'With', as in cum dividend, where security purchases include rights to the next dividend payment, and cum rights, where shares are traded with rights, such as to a scrip issue, attached.
current account
Record of transactions between two parties. For example, between a bank and its customer or a branch and its head office.
current asset
Asset which satisfies any of the following criteria: (a) is expected to be realised in, or is intended for sale or consumption in, the entity's normal operating cycle; (b) is held primarily for the purpose of being traded; (c) is expected to be realised within twelve months of the balance sheet date; or (d) is cash or cash equivalent (IAS 1).
current cost accounting (CCA)
Method of accounting in which profit is defined as the surplus after allowing for price changes on the funds needed to continue the existing business and to maintain its operating capability, whether financed by shares or borrowing. A CCA balance sheet shows the effect of physical capital maintenance.
current liability
Liability which satisfies any of the following criteria: (a) is expected to be settled in the entity's normal operating cycle; (b) is held primarily for the purpose of being traded; or (c) is due to be settled within twelve months of the balance sheet date. All other liabilities are classified as non-current (IAS 1).
current purchasing power accounting (CPP)
Method of accounting in which the values of non-monetary items in the historical cost financial statements are adjusted, using a general price index, so that the resulting profit allows for the maintenance of the purchasing power of the shareholders' interest in the entity. A CPP balance sheet shows the effect of financial capital maintenance.
current tax
Amount of income taxes payable (or recoverable) in respect of the taxable profit (or loss) for a period (IAS 12).
customer account profitability
Analysis of the revenue streams and service costs associated with specific customers or customer groups.
Method of analysing the profits of an organisation by attributing costs and revenues to customers, rather than to products (as in direct product profitability).
customer profitability analysis (CPA)
Analysis of the revenue streams and service costs associated with specific customers or customer groups.
customer relationship management (CRM)
A culture, possibly supported by appropriate information systems, where emphasis is placed on the interfaces between the entity and its customers. Knowledge is shared, within the entity, to ensure that the customer receives a consistently high service level.
date of transition (to IFRSs)
Beginning of the earliest period for which an entity presents full comparative information under IFRSs in its first IFRS-compliant financial statements (IFRS 1).
debt capacity
Extent to which an entity can support and/or obtain loan finance.
debtor
See receivables.
decision tree
Pictorial method of showing a sequence of interrelated decisions and their expected outcomes. Decision trees can incorporate both the probabilities of, and values of, expected outcomes, and are used in decision making.
See Figure 2.2.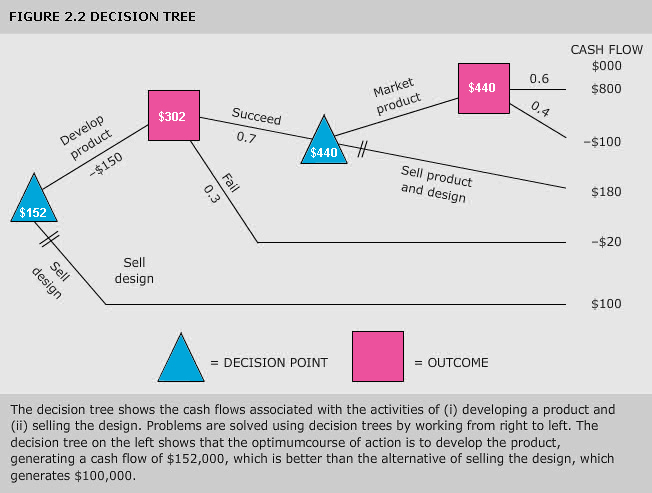
deductible temporary difference
Temporary difference that will result in amounts that are deductible in determining taxable profit (or tax loss) of future periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled (IAS 12).
deep discount bond
Bond offered at a large discount on the face value of the debt so that a significant proportion of the return to the investor comes by way of a capital gain on redemption, rather than through interest payments.
deferred expenditure
Expenditure not charged against income in an accounting period but carried forward as a non-current or current asset to be charged in one or more subsequent periods, for example development expenditure (refer to IAS 38).
deferred tax
Difference between the tax ultimately payable on the profits recognised in an accounting period and the actual amount of tax payable for the same accounting period. The former figure will be based on the tax implications of accounting profit and the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities. The latter figure will be based on a calculation of profits as recognised by the tax authorities.
deferred tax asset
Amount of income taxes recoverable in future periods in respect of deductible temporary differences, carried forward unused tax losses and unused tax credits (IAS 12).
deferred tax liability
Amount of income taxes payable in future periods in respect of taxable temporary differences (IAS 12).
defined benefit plan
Any post-employment scheme other than a defined contribution plan (IAS 19). In such a scheme the employer takes the risk—also known as a final salary scheme.
defined contribution plan
Post-employment benefit plan under which an entity pays fixed contributions into a separate entity (the fund) and will have no legal or constructive obligation to pay further contributions, if the fund does not hold sufficient assets to pay all employee benefits relating to their service in the current and prior periods (IAS 19). In such a scheme the employee takes the risk—also known as a money purchase scheme.
depreciable amount
Cost of an asset, or other amount substituted for cost, less the residual value (IAS 16).
depreciation
Systematic allocation of the depreciable amount of an asset over its useful life (IAS 16). Normally applied to tangible assets.
See amortisation.
deprival value
Basis for valuing assets based on the maximum amount which an entity would be willing to pay rather than forgo the asset. Deprival value is the lower of replacement cost and recoverable amount (itself the higher of fair value less costs to sell and value in use).
See impairment.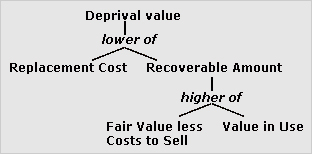
de-recognition
Removal of a previously recognised asset (or liability) from an entity's balance sheet.
development costs
Costs incurred in applying research findings or other knowledge to a plan or design for the production of new or substantially improved materials, devices, products, processes, systems or services prior to the commencement of commercial production or use (IAS 38).
dilution
Reduction in the earnings and voting power per share caused by an increase or potential increase in the number of shares in issue. For the purpose of calculating diluted earnings per share, the profit attributable to ordinary shareholders and the weighted average number of shares outstanding should be adjusted for the effects of all dilutive potential ordinary shares.
Also See anti-dilution.
direct product profitability (DPP)
Used primarily within the retail sector, DPP involves the attribution of both the purchase price and other indirect costs (for example distribution, warehousing and retailing) to each product line. Thus a net profit, as opposed to a gross profit, can be identified for each product. The cost attribution process utilises a variety of measures (for example warehousing space and transport time) to reflect the resource consumption of individual products.
discontinued operation
Component of an entity that has either been disposed of or is classified as held for sale and: (a) represents, or is part of a single plan to dispose of, a separate major line of business or geographical area of operations; or (b) is a subsidiary acquired exclusively with a view to resale (IFRS 5).
See Figure 3.5. 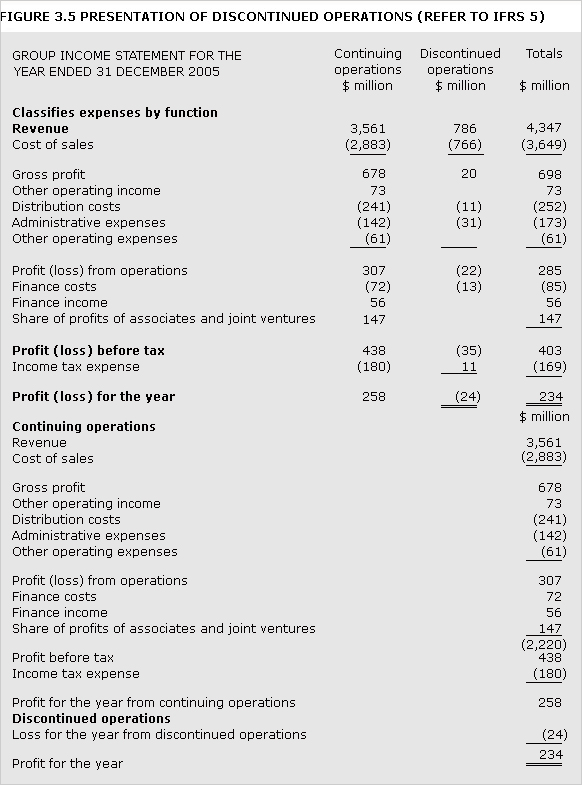
discount rate (capital investment appraisal)
Percentage rate used to discount future cash flows generated by a capital project.
discounted cash flow (DCF)
Discounting of the projected net cash flows of a capital project to ascertain its return or present value. The methods commonly used are:
discounted payback: The discount rate is used to calculate the present values of periodic cash flows with a payback period then being calculated.
net present value (NPV): The discount rate is chosen and the present value is expressed as a sum of money.
yield, or internal rate of return (IRR): The calculation determines the return in the form of a percentage.
See capital investment appraisal, net present value, internal rate of return and discounted payback.
discounted payback
Capital investment method with the aim of determining the period of time required to recover initial cash outflow when net cash inflows are discounted at the opportunity cost of capital.
Also see payback and discounted cash flow.
disposal group
Group of assets to be disposed of, by sale or otherwise, together as a group in a single transaction, and liabilities directly associated with those assets that will be transferred in the transaction (IFRS 5).
distributable reserves
Profit for a period, plus retained earnings from previous periods, that are available for payment as dividends (or other distributions to owners). The split between distributable and non-distributable reserves is a UK legal requirement to ensure that creditors have some protection from the effects of losses.
distribution costs
Cost of warehousing saleable products and delivering them to customers. These costs are reported in the income statement.
divestment
Disposal of part of its activities by an entity.
dividend
Distribution of profits to the holders of equity investments in proportion to their holdings of a particular class of capital (IAS 18).
dividend growth model
Way of assessing the value of shares by capitalising future dividends that grow at a constant rate.
dividend yield

Post-tax dividend return on market value offered by the shares shown as a percentage.
documentary credit
Arrangement, used in the finance of international transactions, whereby a bank undertakes to make a payment to a third party on behalf of a customer.
dominant influence
Influence that can be exercised over an entity to achieve the operating and financial policies designed by the holder of the influence, notwithstanding the rights or influence of any other party.
double-entry bookkeeping/accounting
Most commonly used system of bookkeeping based on the principle that every financial transaction involves the simultaneous receiving and giving of value, and is therefore recorded twice.
double taxation agreement
Agreement between two countries intended to avoid the double taxation of income which would otherwise be subject to taxation in both.
doubtful debts provision
Amount charged against profit and deducted from trade receivables to allow for the estimated non-recovery of a proportion of the trade receivables.
See bad debt.
downsizing
Organisational restructuring involving outsourcing activities, replacing permanent staff with contract employees and reducing the number of levels within the organisational hierarchy, with the intention of making the entity more flexible, efficient and responsive to its environment.
earnings per share, basic
Profit for the period that is attributable to ordinary shareholders (the numerator) divided by the weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding during the period (the denominator) (IAS 33).
earnings per share, diluted
Basic earnings per share with both the numerator and the denominator adjusted for the effects of all dilutive potential ordinary shares (refer to IAS 33).
earnings yield

As a percentage, indicates the total amount earned in respect of each equity share in issue, in relation to the market price of the share. The earnings yield computation can also be based on the aggregate earnings and the market value of the equity capital.
earn-out arrangement
Procedure whereby owners/managers selling an entity receive a portion of their consideration linked to the financial performance of the business during a specified period after the sale. The arrangement gives a measure of security to the new owners, who pass some of the financial risk associated with the purchase of a new enterprise to the sellers.
economic exposure
Risk that a company's future cash flows will vary as a result of changes in exchange rates.
economic order quantity (EOQ)
Most economic stock replenishment order size, which minimises the sum of stock ordering costs and stockholding costs. EOQ is used in an 'optimising' stock control system. EOQ may be calculated as: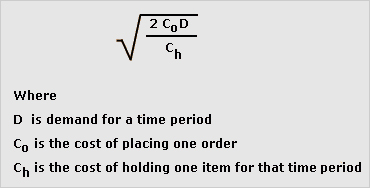
economic value added (EVA)
Profit less a charge for capital employed in the period. Accounting profit may be adjusted, for example, for the treatment of goodwill and research and development expenditure, before economic value added is calculated (Stern Stewart & Co).
economies of scale
Reductions in unit average costs caused by increasing the scale of production.
economies of scope
Reduction in unit average costs caused by the simultaneous production of a number of related products, permitting benefits such as the sharing of joint costs over a larger volume than would otherwise be possible.
economy
Acquisition of resources of appropriate quantity and quality at minimum cost.
See Figure 2.3.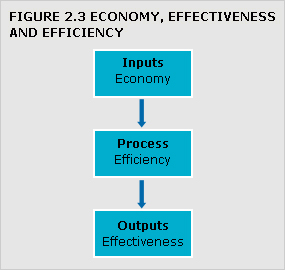
effectiveness
Utilisation of resources such that the output of the activity achieves the desired result.
See Figure 2.3.
efficiency
Achievement of either maximum useful output from the resources devoted to an activity or the required output from the minimum resource input.
See Figure 2.3.
efficient markets hypothesis
Hypothesis that the stock market responds immediately to all available information with the effect that an individual investor cannot, in the long run, expect to obtain greater than average returns from a diversified portfolio of shares. There are three forms:
weak form: Market in which security prices instantaneously reflect all information on past price and volume changes in the market.
semi-strong form: Market in which security prices reflect all publicly available information.
strong form: Market in which security prices reflect instantaneously all information available to investors whether publicly available or otherwise.
electronic funds transfer
System used by the banking sector for the movement of funds between accounts and for the provision of services to the customer.
employee benefits
All forms of consideration given by an entity in exchange for service rendered by employees (IAS 19).
enterprise resource planning (ERP)
Software system designed to support and automate the business processes of medium and large enterprises. ERP systems are accounting oriented information systems which aid in identifying and planning the enterprise wide resources needed to resource, make, account for and deliver customer orders. Initially developed from MRP II systems, ERP tends to incorporate a number of software developments such as the use of relational databases, object-oriented programming and open system portability.
entity
Economic unit that has a separate, distinct identity, for example an industrial or commercial company (or enterprise), charity, local authority, government agency or fund.
environmental impact assessment
Study which considers potential environmental effects during the planning phase before an investment is made or an operation started.
environmental management accounting
Identification, collection, analysis and use of two types of information for internal decision making: physical information on the use, flows and rates of energy, water and materials (including wastes); and monetary information on environment-related costs, earnings and savings (EMARIC).
environmental reporting
Report or disclosure by an entity that discusses and/or quantifies the benefits and costs of the entity's interaction with its operating environment.
equity
Residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities (IASB Framework). It is comprised of share capital, retained earnings and other reserves of a single entity, plus minority interests in a group, representing the investment made in the entity by its owners.
equity instrument
Contract that evidences a residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting all of its liabilities (IAS 32).
equity method of accounting
Method of accounting whereby the investment is initially recognised at cost and adjusted thereafter for the post-acquisition change in the investor's share of the net assets of the investee. The profit or loss of the investor includes the investor's share of the profit or loss of the investee. A method used to account for associates and (optionally) joint ventures (refer to IAS 28 and IAS 31).
equity shares
See ordinary shares
equivalent units
Notional whole units representing uncompleted work. Used to apportion costs between work in progress and completed output, and in performance assessment.
eurobond
Bond sold outside the jurisdiction of the country in whose currency the bond is denominated.
eurodollars
US dollars deposited with, or borrowed from, a bank outside the US.
events after the balance sheet date
Events, favourable and unfavourable, that occur between the balance sheet date and the date the financial statements are authorised for issue.
adjusting events: Those that provide evidence of conditions that existed at the balance sheet date.
non-adjusting events: Those that are indicative of conditions that arose after the balance sheet date. (Refer to IAS 10).
ex
'Without', as in ex dividend, where security purchases do not include rights to the next dividend payment, and ex rights, where rights attaching to share ownership, such as a scrip issue, are not transferred to a new purchaser.
exceptional items
Material items which derive from events or transactions that should be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements by virtue of their size or incidence in relation to the income statement.
exchange controls
Restrictions in the convertibility of a currency, generally enforced by central banks on the instruction of national governments.
exchange difference
Difference (profit or loss) resulting from translating a given number of units of one currency into another currency at different exchange rates (IAS 21).
exchange rate
Rate at which a national currency exchanges for other national currencies, being set by the interaction of demand and supply of the various currencies in the foreign exchange market (floating exchange rate), or by government intervention in order to maintain a constant rate of exchange (fixed exchange rate).
closing rate: Spot transactions ruling at the balance sheet date, being the mean of the buying and selling rates at the close of business on the day for which the rate is to be ascertained.
forward exchange rate: Set for the exchange of currencies at some future date.
spot exchange rate: Set for the immediate delivery of a currency.
exercise price
The price at which an option to purchase or to sell shares or other items (call option or put option) may be exercised.
See call option, put option.
expected value/payoff
Financial forecast of the outcome of a course of action multiplied by the probability of achieving that outcome. The probability is expressed as a value ranging from 0 to 1.
externalities
Benefits or costs arising from an activity which does not accrue to the entity or person carrying on the activity.
factoring
Sale of debts to a third party (the factor) at a discount in return for prompt cash. A factoring service may be with recourse, in which case the supplier takes the risk of the debt not being paid, or without recourse when the factor takes the risk.
See invoice discounting.
fair value
Amount for which an asset could be exchanged, or a liability settled, between knowledgeable and willing parties in an arm's length transaction (IAS 2).
fair value less costs to sell
Amount obtainable from the sale of an asset (or cash generating unit) in an arm's length transaction between knowledgeable and willing parties, less the direct costs of disposal (IAS 36).
feasible region
Area contained within all of the constraint lines shown on a graphical depiction of a linear programming problem. All feasible combinations of output are contained within or located on the boundaries of the feasible region.
See Figure 1.19. 
first in, first out (FIFO)
See stock (inventory) valuation
financial accounting
Classification and recording of the monetary transactions of an entity in accordance with established concepts, principles, accounting standards and legal requirements and their presentation, by means of income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements, during and at the end of an accounting period.
financial asset
Any asset that is: (a) cash; (b) an equity instrument of another entity; (c) a contractual right: (i) to receive cash or another financial asset from another entity, or (ii) to exchange financial assets or financial liabilities with another entity under conditions that are potentially favourably to the entity; or (d) a contract that will or may be settled in the entity's own equity instruments and is: (i) a non-derivative for which the entity is or may be obliged to receive a variable number of the entity's own equity instruments, or (ii) a derivative that will or may be settled other than by the exchange of a fixed amount of cash or other financial asset for a fixed number of the entity's own equity instruments (IAS 32).
financial control
Control of the performance of an entity by setting a range of financial targets and the monitoring of actual performance towards these targets.
financial instrument
Any contract that gives rise to a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability of another entity (IAS 32).
financial instrument, derivative
Financial instrument or other contract with all three of the following characteristics: (a) its value changes in response to the change in a specified interest rate, financial instrument price, commodity price, foreign exchange rate, index of prices or rates, credit rating or credit index, or other variable, provided in the case of a non-financial variable that the variable is not specific to a party to the contract (sometimes called the underlying); (b) it requires no initial net investment or an initial net investment that is smaller than would be required for other types of contracts that would be expected to have a similar response to changes in market forces; and (c) it is settled at a future date (IAS 39).
financial leverage/gearing
Amount of debt, in relation to equity, in the capital structure of an entity or debt interest in relation to profit. An entity with no gearing has no debt.
financial liability
Any liability that is: (a) a contractual obligation: (i) to deliver cash or another financial asset to another entity; or (ii) to exchange financial assets or financial liabilities with another entity under conditions that are potentially unfavourable to the entity; or (b) a contract that will or may be settled in the entity's own equity instruments and is: (i) a non-derivative for which the entity is or may be obliged to deliver a variable number of the entity's own equity instruments; or (ii) a derivative that may or will be settled other than by the exchange of a fixed amount of cash or another financial asset for a fixed amount of the entity's own equity instruments (IAS 32).
financial management
Management of all the processes associated with the efficient acquisition and deployment of both short- and long-term financial resources.
financial position
Relationship of the assets, liability and equity of an entity as reported in its balance sheet (IASB Framework).
Financial Reporting Council (FRC)
UK's single independent regulator of financial reporting and corporate governance with delegated statutory powers. The FRC oversees the work of the Accounting Standards Board (ASB), the Financial Reporting Review Panel (FRRP), the Professional Oversight Board for Accountancy, the Auditing Practices Board (APB) and the Accountancy Investigation and Discipline Board.
Financial Reporting Review Panel
UK review panel established to examine contentious departures, by large companies, from accounting standards.
Financial Reporting Standard (FRS)
A UK accounting standard issued since 1 August 1990, when the Accounting Standards Board (ASB) succeeded the Accounting Standards Committee (ASC).
Financial Services Authority (FSA)
An independent body that regulates the financial services industry in the UK, with powers in rule-making, investigation and enforcement. Its broad task is to achieve a marketplace that is run in an efficient, orderly and fair manner whilst ensuring that consumers are properly informed and appropriately protected.
financial statements
Complete set of financial statements comprises: balance sheet, income statement, statement of changes in equity or statement of recognised income and expense, cash flow statement, notes comprising a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory notes.
financing activities
Activities that result in changes in the size and composition of the contributed equity and borrowings of an entity as reported in its cash flow statement (IAS 7).
first in, first out (FIFO)
See stock (inventory) valuation.
fixed charge
Protection given to creditors whereby they can enforce the sale of specified (non-current) asset(s) if there is a default.
flexible manufacturing system (FMS)
Integrated, computer-controlled production system which is capable of producing any of a range of parts, and of switching quickly and economically between them.
floating charge
Protection given to creditors whereby they can enforce the sale of any (non-current) asset(s) if there is a default.
floating rate financial assets and financial liabilities
Financial assets and financial liabilities that attract an interest charge and have their interest rate reset at least once a year. For the purpose of the FRS, financial assets and financial liabilities that have their interest rate reset less frequently than once a year are to be treated as fixed rate financial assets and financial liabilities (FRS 13).
forecast
A prediction of future events and their quantification for planning purposes.
foreign currency transaction
Transaction that is denominated in, or requires settlement in, a foreign currency (IAS 21).
foreign currency translation
Restatement of the transactions or financial statements of a foreign operation into the reporting currency of the parent (or investor) for the purpose of preparing consolidated financial statements.
foreign direct investment (FDI)
Establishment of new overseas facilities or the expansion of existing overseas facilities by an investor. FDI may be inward (domestic investment by overseas companies) or outward (overseas investment by domestic companies).
foreign operation
An entity that is a subsidiary, associate, joint venture or branch of the reporting entity, the activities of which are based or conducted in a country other than the country of the reporting entity (IAS 21).
forensic accounting
Use of accounting records and documents in order to determine the legality or otherwise of past activities.
forfaiting
Purchase of financial instruments such as bills of exchange or letters of credit on a non-recourse basis by a forfaiter, who deducts interest (in the form of a discount) at an agreed rate for the period covered by the notes. The forfaiter assumes the responsibility for claiming the debt from the importer (buyer) who initially accepted the financial instrument drawn by the seller of the goods. Traditionally, forfeiting is fixed-rate, medium-term (one- to five-year) finance.
See invoice discounting.
forward contract
Agreement to exchange different currencies at a specified future date and at a specified rate. The difference between the specified rate and the spot rate ruling on the date the contract was entered into is the discount or premium on the forward contract (SSAP 20).
free cash flow
Cash flow from operations after deducting interest, tax, preference dividends and ongoing capital expenditure, but excluding capital expenditure associated with strategic acquisitions and/or disposals and ordinary share dividends.
FRSSE
Financial Reporting Standard for Smaller Entities. This is a single standard for an optional simplified reporting regime for smaller entities in the UK.
functional currency
Currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates (IAS 21).
fundamental analysis
Analysis of external and internal influences that directly affect the operations of a company with a view to assisting in investment decisions. Information accessed might include fiscal/monetary policy, financial statements, industry trends and competitor analysis.
See technical analysis.
fungible assets
Assets which are substantially indistinguishable one from another, for example a holding of shares in an entity.
futures contract
Contract relating to currencies, interest rates, commodities or shares that obliges the buyer (seller) to purchase (sell) the specified quantity of the item represented in the contract at a predetermined price at the expiration of the contract. Unlike forward contracts, which are entered into privately, futures contracts are traded on organised exchanges, carry standard terms and conditions, have specific maturities and are subject to rules concerning margin requirements.
futures market
Exchange-traded market for the purchase or sale of a standard quantity of an underlying item such as currencies, commodities or shares for settlement at a future date at an agreed price.
gap analysis
A comparison between an entity's desired future performance level (most commonly expressed in terms of profit or ROCE) and the expected performance of projects both planned and underway. Differences are classified in a way which aids the understanding of performance, and which facilitates improvement.
generally accepted accounting practice (GAAP)
Components of UK GAAP include: the provisions of company law; the accounting standards issued by the ASB; UITF Abstracts; Statements of Recommended Practice; stock exchange listing roles; professional recommendations and pronouncements of the Financial Reporting Review Panel. For matters not covered by these, the practices of leading companies and audit firms are widely accepted as possessing authority.
generic strategies
See three generic strategies.
geographic segment
Distinguishable component of an entity that is engaged in providing products or services within a particular economic environment and that is subject to risks and returns that are different from those of components operating in other economic environments (IAS 14).
See business segment
goal congruence
In a control system, the state which leads the individuals or groups to take actions which are in their self-interest and also in the best interest of the entity. Goal incongruence exists when the interests of individuals or of groups associated with an entity are not in harmony.
goodwill
acquired: Future economic benefits arising from assets that are not capable of being individually identified and separately recognised (refer to IFRS 3).
positive goodwill: Excess of the purchase consideration over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired.
negative goodwill: Excess of the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired over the purchase consideration.
internally generated: An entity's own view of its value above its recorded value which cannot be recognised in financial statements prepared in accordance with accounting standards.
Governance, Combined Code on Corporate
Guidance on good governance for UK listed companies, published in July 2003 and consolidating earlier voluntary corporate governance codes (Cadbury, Greenbury, Hampel, Higgs and Smith). The Combined Code is annexed to the Listing Rules of the UK Listing Authority, the FSA (Financial Services Authority). Listed companies are required to state whether they comply with the Code, and justify any departures.
governance, corporate
The system by which companies and other entities are directed and controlled. The boards of directors are responsible for the governance of their companies and other entities. The shareholders' role in governance is to appoint the directors and the auditors, and to satisfy themselves that an appropriate governance structure is in place. The responsibilities of the board include setting the company's (or entity's) strategic aims, providing the leadership to put them into effect, supervising the management of the company (or entity) and reporting to shareholders on their stewardship. The board's actions are subject to laws, regulations and the shareholders in general meeting.
governance, enterprise
Set of responsibilities and practices exercised by the board and executive management with the goal of providing strategic direction, ensuring that objectives are achieved, ascertaining that risks are managed appropriately and verifying that the organisation's resources are used responsibly (Information Systems Audit and Control Foundation).
Governance, OECD Principles of Corporate
Framework for good practice which has been agreed by the governments of all OECD member countries. They have been designed to assist governments and regulatory bodies in both OECD countries and elsewhere in drawing up and enforcing effective rules, regulations and codes of corporate governance. In parallel, they provide guidance for stock exchanges, investors, companies (and other entities) and others that have a role in the process of developing good corporate governance.
government grants
Assistance by the government (including local, national and international agencies) in the form of transfer of resources to an entity in return for past or future compliance with certain conditions relating to the operating activities of the entity (IAS 20).
gross profit percentage
See ratio, gross profit to sales revenue.
group
A parent and all its subsidiaries (IAS 27).
group accounts
See consolidated financial statements.
hedge
Transaction to reduce or eliminate an exposure to risk.
hedge effectiveness
Degree to which changes in the fair value or cash flows of the hedged item that are attributable to a hedged risk are offset by changes in the fair value or cash flows of the hedging instrument (IAS 39).
hedge funds
Generally actively managed with greater freedom than conventional mutual funds to borrow heavily and use high-risk investment strategies, such as selling short and using derivatives, to make absolute returns even in falling markets.
hedged instrument
Designated derivative whose fair value or cash flows are expected to offset changes in the fair value or cash flows of a designated hedged item (IAS 39).
hedged item
Asset, liability, firm commitment, highly probable forecast transaction or net investment in a foreign operation that exposes the entity to risks of changes in fair value or future cash flows and is designated as being hedged (IAS 39).
held-to-maturity investment
Non-derivative financial assets with fixed or determinable payments and fixed maturity that an entity has the positive intention and ability to hold to maturity (IAS 39).
high/low method
Method of estimating cost behaviour by comparing the total costs associated with two different levels of output. The difference in costs is assumed to be caused by variable costs increasing, allowing unit variable cost to be calculated. Following from this, since total cost is known, the fixed cost can be derived.
hire purchase contract
A contract for the hire of an asset that contains a provision giving the hirer an option to acquire title to the asset upon the fulfilment of agreed conditions (IAS 17).
historical cost
For assets—recorded at the amount of cash (or cash equivalents) paid or the fair value of the consideration given to acquire them at the time of their acquisition. For liabilities—recorded at the amount of proceeds received in exchange for the obligation (for example, income taxes) or at the amounts of cash (or cash equivalents) expected to be paid to satisfy the liability in the normal course of business. (Refer to IASB Framework.)
historical cost accounting
System of accounting in which all values are based on the historical costs incurred.
horizontal group
Position where two or more undertakings are controlled by a common parent, such as a private individual, who is not subject to the requirements of regulations or corporate laws. There is therefore no legal or professional mechanism which can be used to require the preparation of consolidated financial statements.
See consolidated financial statements.
human resource accounting
Identification, recording and reporting of the investment in, and return from the employment of, the personnel of an entity.
hurdle rate
Rate of return which a capital investment proposal must achieve if it is to be accepted. Set by reference to the cost of capital, the hurdle rate may be increased above the basic cost of capital to allow for different levels of risk.
hyperinflation
Loss of purchasing power of money at such a rate that comparison of amounts from transactions and other events that have occurred at different times, even within the same accounting period, is misleading (IAS 29). As an indication, hyperinflation could exist where the cumulative inflation rate over three years is 100%.
identifiable assets and liabilities
Assets and liabilities of an entity that are capable of being disposed of or settled separately, without disposing of a business of the entity (FRS 10).
impairment
Reduction in the carrying value of a non-current asset where its recoverable amount (the higher of fair value less costs to sell and value in use) is less than its existing carrying amount.
imprest system
Method of controlling cash or inventory. When the cash or inventory has been reduced by disbursements or issues it is restored to its original level.
inception of a lease
Earlier of the date of the lease agreement and the date of commitment by the parties to the principal provisions of the lease (IAS 17).
income
Increases in economic benefits during an accounting period in the form of inflows or enhancements of assets, or decreases of liabilities that result in increases in equity, other than those relating to contributions from equity holders (IASB Framework).
income and expenditure account
Financial statement for not-for-profit entities such as clubs, associations and charities. It shows the surplus or deficit, being the excess of income over expenditure or vice versa, for a period and is drawn up on the same accruals basis as an income statement.
income statement
Financial statement including all the profits and losses recognised in a period, unless an accounting standard requires inclusion elsewhere (refer to IAS 1).
See Figure 3.6. 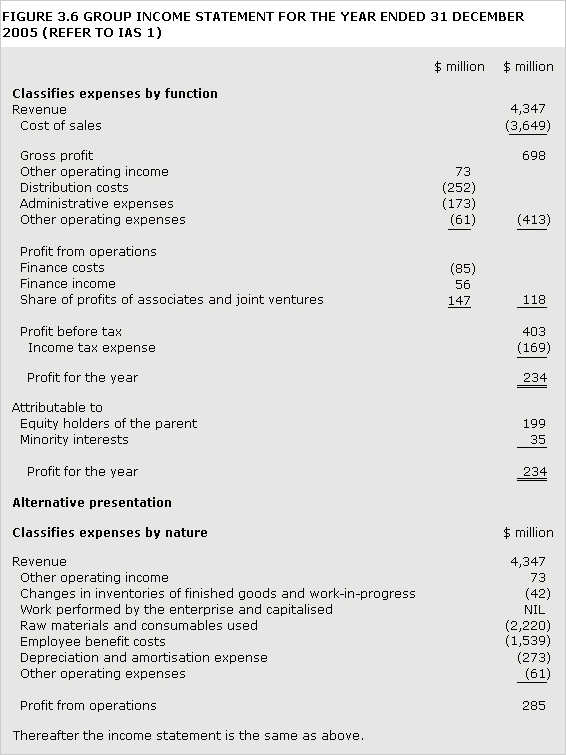
incomplete records
Accounting system which is not double-entry bookkeeping. Various degrees of incompleteness can occur, for example single-entry bookkeeping, in which usually only a cash book is maintained.
incremental analysis
Analysis of changes in costs and revenues caused by a change in activity. A significant change may cause changes to variable and fixed costs and possibly to selling prices. Incremental or differential costs and revenues are compared to determine the financial effect of the change.
incremental yield
Measure used in capital investment appraisal where a choice lies between two projects. A rate of return is calculated for the difference between the cash flows of the projects.
inflation
General increase in the price level over time measured by a retail price index.
insolvency
Inability of a debtor to pay debts when they fall due.
intangible assets
Identifiable non-monetary asset without physical substance which must be controlled by the entity as the result of past events and from which the entity expects a flow of future economic benefits (refer to IAS 38).
intellectual capital
Knowledge which can be used to create value. Intellectual capital includes:
human resources: The collective skills, experience and knowledge of employees;
intellectual assets: Knowledge which is defined and codified such as drawing, computer program or collection of data; and
intellectual property: Intellectual assets which can be legally protected such as patents and copyrights.
interest rate parity theory
Method of predicting foreign exchange rates based on the hypothesis that the difference between the interest rates in two countries should offset the difference between the spot rates and the forward foreign exchange rates over the same period.
interest yield
Annual rate of interest earned on a security, excluding the effect of any increase in price to maturity.
inter-firm comparison
Systematic and detailed comparison of the performance of different entities generally operating in a common industry. Entities participating in such a scheme normally provide standardised, and therefore comparable, information to the scheme administrator, who then distributes to participating members only the information supplied by participants. Normally the information distributed is in the form of ratios, or in a format which prevents the identity of individual scheme members from being identified.
interim financial report
Financial report containing either a complete set of financial statements or a set of condensed financial statements for an interim period (one shorter than a full financial year) (refer to IAS 34).
internal check
Procedures designed to provide assurance that: a) everything which should be recorded has been recorded; (b) errors or irregularities are identified; and (c) assets and liabilities exist and are correctly recorded.
internal control
Management system of controls, financial and otherwise, established in order to provide reasonable assurance of: (a) effective and efficient operation; (b) internal financial control; and (c) compliance with laws and regulations.
Good internal control systems should make accounting records more reliable and the occurrence of fraud and error more difficult.
internal financial control
Internal controls established in order to provide reasonable assurance of: (a) the safeguarding of the entity's assets against unauthorised use or disposal; and (b) the maintenance of proper accounting records and the reliability of financial information used within the entity or for publication.
internal rate of return (IRR)
Annual percentage return achieved by a project, at which the sum of the discounted cash inflows over the life of the project is equal to the sum of the discounted cash outflows.
See discounted cash flow.
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
Has sole responsibility for the development and publication of IFRSs. Seeks to develop a single set of high quality global Accounting Standards requiring transparent and comparable information in general purpose financial statements. Over 90 countries will either require or permit the use of the IASB's Standards and Interpretations for domestically listed entities by 2007.
Also see Standards Advisory Council (SAC) and International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (IFRIC).
International Accounting Standards Committee Foundation (IASCF)
Selects, oversees and funds the IASB and its two advisory bodies (IFRIC, SAC) under the direction of its Trustees.
International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB)
Independent standard setting body under the auspices of the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC). The IAASB issues:
- International Standards on Auditing (ISAs);
- International Standards on Assurance Engagements (ISAEs);
- International Standards on Related Services (ISRSs); and
- International Standards on Quality Control (ISQCs).
International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (IFRIC)
Assists the IASB in improving standards of financial accounting and reporting. This is achieved by providing timely guidance on newly identified financial reporting issues not specifically addressed by IFRSs or where unsatisfactory or conflicting interpretations have developed or seem likely to develop.
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs)
Standards and Interpretations published or adopted by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). They comprise:
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs)
- International Accounting Standards (IASs)
- Interpretations originated by the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (IFRIC) or the former Standing Interpretations Committee (SIC).
inventories
Assets held for sale in the ordinary course of business in the process of production for such a sale or in the form of materials or supplies to be consumed in the production process or in the rendering of services (IAS 2). Synonym for stock.
investing activities
Acquisition and disposal of long-term (non-current) assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents as reported in the entity's cash flow statement (IAS 7).
investment
Any application of funds which is intended to provide a return by way of interest, dividend or capital appreciation.
investment property
Property (land or building or part of a building) held by the owner (or by the lessee under a finance lease) to earn rentals and/or for capital appreciation (IAS 40).
invoice discounting
Sale of debts to a third party at a discount in return for prompt cash. The administration is managed in such a way that the debtor is generally unaware of the discounter's involvement and continues to pay the supplier.
See factoring and forfaiting.
ISO 9000
Quality system standard which requires complying organisations to operate in accordance with a structure of written policies and procedures that are designed to ensure the consistent delivery of a product or service to meet customer requirements.
issue costs
The costs that are incurred directly in connection with the issue of a capital instrument, that is, those costs which would have not been incurred if the specific instrument in question had not been issued (FRS 4).
job
Customer order or task of relatively short duration.
job cost sheet
Detailed record of the amount, and cost, of the labour, material and overhead charged to a specific job.
joint products
Two or more products produced by the same process and separated in processing, each having a sufficiently high saleable value to merit recognition as a main product.
See by-product.
joint control—joint venture
Contractually agreed sharing of control over an economic activity which exists only when the strategic and operating decisions relating to the activity require the unanimous consent of the parties sharing control (the venturers) (IAS 31).
joint control—related parties
Contractually agreed sharing of control over an economic activity (IAS 24).
joint venture
Contractual arrangement whereby two or more parties undertake an economic activity which is subject to joint control (IAS 31).
junk bond
High-yielding bond issued on low-grade security. The issue of junk bonds has most commonly been linked with takeover activity. Bonds may also assume junk status when the issuer is at risk of insolvency.
just-in-time (JIT)
Quality system standard which requires complying organisations to operate in accordance with a structure of written policies and procedures that are designed to ensure the consistent delivery of a product or service to meet customer requirements.
kaizen
Japanese term for continuous improvement in all aspects of an entity's performance at every level.
See continuous improvement.
key management personnel
Those persons having authority and responsibility for planning, directing and controlling the activities of the entity, directly or indirectly, including any director (whether executive or otherwise) of that entity (IAS 24).
key performance indicators (KPIs)
Quantitative but not necessarily financial metrics that can indicate progress or lack of progress towards a strategic objective. For example, metrics may be devised for safety, quality, turnover of key staff. Key performance indicators were important to the idea of management by objectives and are integral to the scorecard ideas developed in the 1990s.
knowledge management
Systematic process of finding, selecting, organising, distilling and presenting information so as to improve comprehension of a specific area of interest. Specific activities help focus the organisation on acquiring, storing and utilising knowledge for such things as problem solving, dynamic learning, strategic planning and decision making.
last in, first out (LIFO)
See stock (inventory) valuation.
lead time
Time interval between the start of an activity or process and its completion, for example the time between ordering goods and their receipt, or between starting production of a product and its completion. The latter is also known as process time.
learning curve
Mathematical expression of the commonly observed effect that, as complex and labour-intensive procedures are repeated, unit labour times tend to decrease. The equation (see Figure 1.20) usually relates the average time taken per unit/batch to the cumulative number of units/batches produced. An alternative, little used, formulation uses the same equation but relates the incremental (not average) time for the nth unit to the cumulative number of units/batches produced. 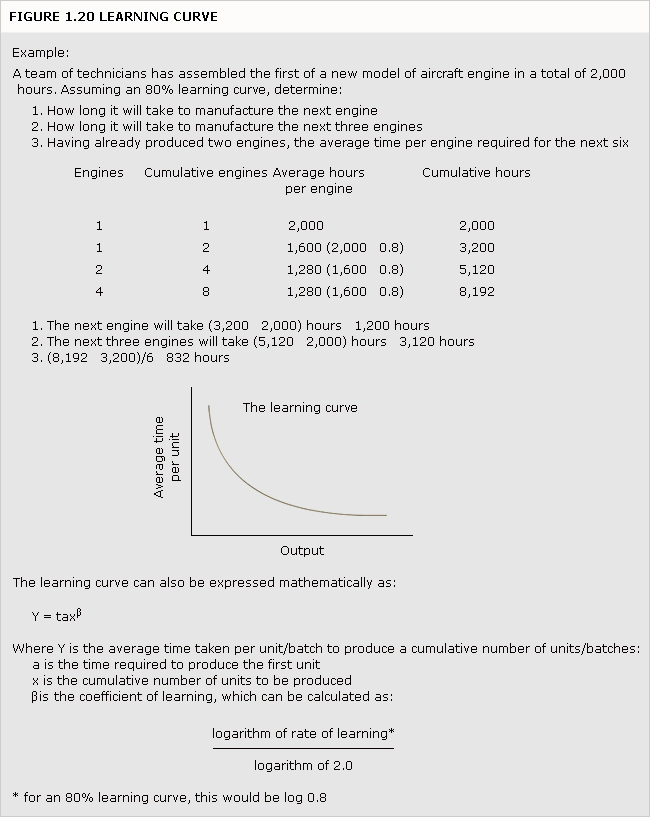
legal obligation
Obligation that derives from: (a) contract (through its explicit or implicit terms); (b) legislation; (c) or other operation of law (IAS 37).
lease
Agreement whereby the lessor conveys to the lessee, in return for a payment or series of payments, the right to use an asset for an agreed period of time (IAS 17).
lease term
Non-cancellable period for which the lessee has contracted to lease the asset together with any further term for which the lessee has the option to continue to lease the asset, with or without further payment, which at the inception of the lease it is reasonably certain that the lessee will exercise (IAS 17).
lease, finance
Lease agreement that transfers substantially all the risks and rewards incidental to ownership of an asset from the lessor to the lessee. Title in the asset may or may not eventually be transferred (IAS 17).
lease, operating
Lease agreement other than a finance lease (IAS 17).
liability
Present obligation of the entity arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the entity of resources embodying economic benefits (IAS 37).
liability method
Method of computing deferred tax by calculating it at the rate of income tax that it is estimated will be applied in the period when the temporary difference reverses. This means the liability is measured at the amount of income tax that it is estimated will be paid or recovered.
limiting factor or key factor
Anything which limits the activity of an entity. An entity seeks to optimise the benefit it obtains from the limiting factor. Examples are a shortage of supply of a resource or a restriction on sales demand at a particular price.
See bottleneck.
liquid assets
Cash, cash equivalents and other assets readily convertible into cash, for example short-term investments.
liquidation
Winding up of a company, in which the assets are sold, liabilities settled as far as possible and any remaining cash returned to the members. Liquidation may be voluntary or compulsory.
liquidity
Availability of sufficient funds to meet financial commitments as they fall due (refer to IAS 30).
loans and receivables
Non-derivative financial assets with fixed or determinable payments that are not quoted in an active market (IAS 39).
London interbank offered rate (LIBOR)
Rate of interest at which banks borrow funds in the London interbank market for a given maturity, normally ranging between overnight and one year.
London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange (LIFFE)
The combined French, Belgian, Portuguese and Dutch exchange operator. Now known as Euronext.liffe since its takeover in 2002 by Euronext.
management accounting
Management accounting is the application of the principles of accounting and financial management to create, protect, preserve and increase value for the stakeholders of for-profit and not-for-profit enterprises in the public and private sectors. Management accounting is an integral part of management. It requires the identification, generation, presentation, interpretation and use of relevant information to: inform strategic decisions and formulate business strategy; plan long, medium and short-run operations; determine capital structure and fund that structure; design reward strategies for executives and shareholders; inform operational decisions; control operations and ensure the efficient use of resources; measure and report financial and non-financial performance to management and other stakeholders; safeguard tangible and intangible assets; implement corporate governance procedures, risk management and internal controls.
management buy-in (MBI)
New team of managers makes an offer to an entity to buy the whole entity, a subsidiary or a section of it, with the intention of taking over the entity.
management buy-out (MBO)
Purchase of a business from its existing owners by members of the management team, generally in association with a financing institution. Where a large proportion of the new finance required to purchase the business is raised by external borrowing, the buy-out is described as leveraged.
management by exception
Practice of concentrating on activities that require attention and ignoring those which appear to be conforming to expectations.
Typically, standard cost variances or variances from budget are used to identify those activities that require attention.
Management's Discussion and Analysis (MD&A)
Narrative element of the statutory reporting package required in the US. It is intended to allow users to understand an entity's financial condition, changes in financial condition and results of operations, and is a discussion and analysis of the entity's operations and prospects, by management. It should fulfil the following objectives: (a) to provide a narrative explanation of an entity's financial statements that enables investors to see the company through the eyes of its management; (b) to enhance the overall financial disclosure and provide the context within which financial information should be analysed; and
(c) to provide information about the quality of, and potential variability of, an entity's earnings and cash flow, so that investors can ascertain the likelihood that past performance is indicative of future performance. (SEC Statement About Management's Discussion & Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, Release No. 33-8056, 2002).
margin
Difference between the selling price and cost of sales expressed either as a percentage of sales or as an absolute amount.
See mark-up
marginal revenue
Additional revenue generated from the sale of one additional unit of output.
mark-down
Reduction in the selling price of damaged or slow-selling goods.
market risk premium
Difference between the expected rate of return on a market portfolio and the risk-free rate of return over the same period.
See risk, market/systematic
market share
An entity's sales of a product or service in a specified market expressed as a proportion of total sales by all entities offering that product or service to the market. A planning tool and a performance assessment ratio.
market value added (MVA)
The difference between a company's market value (derived from the share price) and its economic book value (the amount of capital that shareholders and debt holders have committed to the firm throughout its existence, including any retained earnings).
mark-up
Addition to the cost of goods or services which results in a selling price.
maximax criterion
Criterion used to make a choice between alternative strategies. This favours the strategy that might lead to the highest possible profit, irrespective of the probability of that profit actually being achieved and the outcome if it is not successful.
maximax criterion
Criterion used to make a choice between alternative strategies. This favours the strategy that generates the highest profit if the worst outcome occurs.
memorandum of association
Document which, with the articles of association, provides the legal constitution of a company. The memorandum states the name and registered office of the company. It also defines its powers and objects and usually states that the liability of its members is limited.
See articles of association.
merger
Business combination that results in the creation of a new reporting entity formed from the combining parties, in which the shareholders of the combining entities come together in a partnership for the mutual sharing of the risks and benefits of the combined entity, and in which no party to the combination in substance obtains control over any other, or is otherwise seen to be dominant, whether by virtue of the proportion of its shareholders' rights in the combined entity, the influence of its directors or otherwise (FRS 6). However, IFRS 3 Business Combinations requires all business combinations to be accounted for by applying the purchase method which necessitates the identification of a purchaser and seller and so effectively rules out the possibility of using merger accounting as opposed to acquisition accounting. A demerger takes place when the merger process is reversed, and separate entities emerge from the merged body.
minimax regret criterion
Criterion used to make a choice between alternative strategies. This is the difference between the best and worst possible payoff for each option. This criterion favours the strategy that minimises the maximum regret.
minority interest
Portion of the profit or loss (income statement) and net assets (balance sheet) of a subsidiary attributable to equity interests that are not owned, directly or indirectly, by the parent (IFRS 3).
mission
Fundamental objective(s) of an entity expressed in general terms.
mission statement
Published statement, apparently of the entity's fundamental objective(s). This may or may not summarise the true mission of the entity.
monetary items
Units of currency held and assets and liabilities to be received or paid in a fixed or determinable number of units of currency (IAS 21).
money laundering
Funnelling of cash or other funds generated from illegal activities through legitimate financial institutions and businesses to conceal the source of the funds (Anti-Money Laundering, 2nd ed, IFAC, 2004).
money market
Short-term wholesale market for securities usually maturing in less than one year such as certificates of deposit, treasury bills and commercial paper.
moral hazard
Risk that the existence of a contract will cause behavioural changes in one or both parties to the contract. For example, insuring an asset causes its owner to take less care of it.
MRP (material requirements planning)
System that converts a production schedule into a listing of the materials and components required to meet that schedule, so that adequate stock levels are maintained and items are available when needed.
MRP II (manufacturing resource planning)
Expansion of material requirements planning (MRP) to give a broader approach than MRP to the planning and scheduling of resources, embracing areas such as finance, logistics, engineering and marketing.
national competitive advantage (Porter's diamond)
Theory and model, proposed by M. Porter, for identifying why entities may achieve a competitive advantage over their rivals by virtue of being based or domiciled in a particular country. Often known as Porter's diamond, due to the shape of the diagrammatic representation of the model.
negotiable instrument
Document of title which can be freely traded such as a bill of exchange or other certificate of debt.
net assets
Excess of the carrying amount of assets over liabilities. Equivalent to net worth or equity.
net book value
See carrying amount
net present value (NPV)
Difference between the sum of the projected discounted cash inflows and outflows attributable to a capital investment or other long-term project.
See discounted cash flow.
net realisable value (NRV)
See fair valueless costs to sell.
network analysis
Quantitative technique used in project control. The events and activities making up the whole project are represented in the form of a diagram.
critical event: Any event which lies on the critical path.
critical path: Longest path or paths through a network.
event: Start or completion of an activity. In a network an event is represented by a small circle (a node), and an activity by an arrow.
project evaluation and review technique (PERT): Specification of all activities, events, probabilities and constraints relating to a project from which a network is drawn, providing a model of the way the project should proceed.
slack/float time: Time available for an activity over and above that required for its completion.
noise
Random fluctuations that can be mistaken for important information. Noise can confuse or divert attention from relevant information; efficiency in a system is enhanced as the ratio of information to noise increases.
nominal interest rate
Interest rate expressed in money terms.
nominee holding
Shareholding in a company registered in the name of an agent, instead of that of the owner.
non-current asset
Any asset that does not meet the definition of a current asset (IFRS 5). Tangible or intangible asset, acquired for retention by an entity for the purpose of providing a service to the entity and not held for resale in the normal course of trading. Previously known as a fixed asset.
non-executive director
Director of a company (or other entity) who is not involved in the day-to-day running of operations and is therefore expected to provide an independent view on board issues.
non-financial performance measures
Measures of performance based on non-financial information that may originate in and be used by operating departments to monitor and control their activities without any accounting input. Non-financial performance measures may give a more timely indication of the levels of performance achieved than financial measures do, and may be less susceptible to distortion by factors such as uncontrollable variations in the effect of market forces on operations. Non-financial measures are now integrated with financial measures in systems such as the balanced scorecard. Examples of non-financial measures: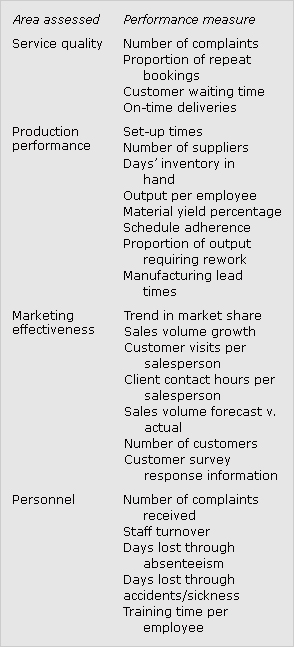
The values expected may vary significantly between industries/sectors.
normal loss
Expected loss, allowed for in the budget, and normally calculated as a percentage of the good output from a process during a period of time. Normal losses are generally either valued at zero or at their disposal values.
notes to financial statements
Contain information in addition to that presented in the balance sheet, income statement, statement of changes in equity and cash flow statement. Notes provide narrative descriptions or disaggregations of items disclosed in those statements and information about items that do not qualify for recognition in those statements (IAS 1).
objectives, hierarchy of
Arrangement of the objectives of an entity into a number of different levels, with the higher levels being more general and the lower more specific. These levels may be mission, goals, targets or, alternatively, strategic objectives, tactical objectives or operational objectives.
obligating event
Event that creates a legal or constructive obligation that results in an entity having no realistic alternative to settling that obligation (IAS 37).
obsolescence
Loss of value of a non-current asset due to advances in technology or changes in market conditions for its product.
off balance sheet finance
Funding or refinancing of an entity's operations in such a way that, under existing legal requirements and accounting practices, some or all of the financing may not be shown on the entity's balance sheet.
offer for sale
An invitation to the public to apply for shares in a company based on information contained in a prospectus.
onerous contract
Contract in which the unavoidable costs of meeting the obligations under the contract exceed the economic benefits expected to be received under it (IAS 37).
operating activities
The principal revenue-producing activities of an entity and other activities not reported elsewhere in the entity's cash flow statement (IAS 7).
Operating and Financial Review (OFR)
Narrative element of the statutory reporting package, from April 2005 required by law for listed companies in the UK. It is a balanced and comprehensive analysis of: (a) the development and performance of the business of the entity during the financial year; (b) the position of the entity at the end of the year; (c) the main trends and factors underlying the development, performance and position of the business of the entity during the financial year; and (d) the main trends and factors which are likely to affect their future development, performance and position, prepared so as to assist investors to assess the strategies adopted by the entity and the potential for those strategies to succeed (ASB Reporting Standard 1: Operating and Financial Review).
operations plans
Fully detailed specifications by which individuals are expected to carry out the predetermined cycles of operations to meet sectoral objectives.
operational gearing
Relationship of fixed cost to total cost of an operating unit. The greater the proportion of total costs that are fixed (high operational gearing), the greater is the advantage to the organisation of increasing sales volume. Conversely, should sales volumes drop, a highly geared organisation would find the high proportion of fixed costs to be a major problem, possibly causing a rapid swing from profitability into loss. Gearing may also be referred to as leverage.
See ratio, gearing/leverage.
option
Right of an option holder to buy or sell a specific asset on predetermined terms on, or before, a future date.
European-style option: Option that can be exercised only at the expiration date.
American-style option: Option that can be exercised at any time prior to expiration.
See call option, put option.
outsourcing
Use of external suppliers as a source of finished products, components or services. This is also known as contract manufacturing or subcontracting.
overhead absorption rate
A means of attributing overhead to a product or service, based for example on direct labour hours, direct labour cost or machine hours.
direct labour cost percentage rate: Overhead absorption rate based on direct labour cost.
direct labour hour rate: Overhead absorption rate based on direct labour hours.
machine hour rate: Overhead absorption rate based on machine hours.
See Figure 1.1.
over the counter (OTC) market
Securities trading carried on outside regulated exchanges. Allows tailor-made transactions.
over/undercapitalisation
Surplus or deficiency of permanent capital in relation to the current level of activity of a business.
Overtrading
The condition of an entity's which enters into commitments in excess of its available short-term resources. This can arise even if an entity is trading profitably, and is typically caused by financing strains imposed by a lengthy operating cycle or production cycle. Undercapitalised new businesses are prone to suffer from overtrading.
par
Nominal value of a bond, being the price denominated for the purpose of setting the interest rate (coupon) payable.
parent
Entity that has one or more subsidiaries (IFRS 3).
Pareto (80/20) distribution
Frequency distribution with a small proportion (for example, 20%) of the items accounting for a large proportion (for example, 80%) of the value/resources. Common occurrences are sales, when 80% of turnover may arise from 20% of customers; inventory, when 20% of the items comprise 80% of the value.
See Figure 2.4. 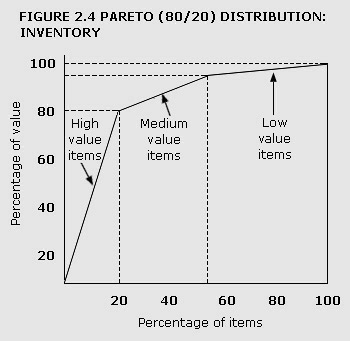
partnership
Relationship which exists between persons carrying on business in common with a view to profit (UK Partnership Act 1890). The liability of the individual partners is unlimited unless the partnership agreement provides for any limitation. The UK Limited Partnership Act 1907 allows a partnership to contain one or more partners with limited liability so long as there is at least one partner with unlimited liability. A partnership consists of not more than twenty persons, except in certain cases, for example practising solicitors, professional accountants and members of the Stock Exchange, where this figure may be exceeded. Other limited partnerships may exist.
partnership, limited liability (LLP)
Legal entity that combines the organisational flexibility and tax status of a partnership with limited liability for its members. This limited liability is possible because an LLP is a legal person separate from its members (UK Limited Liability Partnerships Act 2000).
payables
Person, or an entity, to whom money is owed as a consequence of the receipt of goods or services in advance of payment, known as trade payables in IASs.
payback
Time required for the cash inflows from a capital investment project to equal the cash outflows.
See discounted payback.
payroll analysis
Analysis of labour costs for accounting purposes identifying, for example: gross pay by department, operation or product; and/or gross pay analysed into direct pay or lost time.
percentage of completion method
Method by which construction contract revenue is matched with the contract costs incurred in reaching the stage of completion, resulting in the reporting of revenue, expenses and profit which can be attributed to the proportion of work completed (IAS 11).
performance measurement
Process of assessing the proficiency with which a reporting entity succeeds, by the economic acquisition of resources and their efficient and effective deployment, in achieving its objectives. Performance measures may be based on non-financial as well as on financial information.
See non-financial performance measures.
perpetuity
Periodic payment continuing for a limitless period.
See annuity.
placing
Method of raising share capital in which there is no public issue of shares, the shares being issued, rather, in a small number of large 'blocks', to persons or institutions who have previously agreed to purchase the shares at a predetermined price.
See private placement.
planning
Establishment of objectives, and the formulation, evaluation and selection of the policies, strategies, tactics and action required to achieve them. Planning comprises long-term/strategic planning and short-term/operational planning. The latter is usually for a period of up to one year.
capital funding planning: Process of selecting suitable funds to finance long-term assets and working capital.
capital resource planning: Process of evaluating and selecting long-term assets to meet strategies.
financial planning: Planning the acquisition of funds to finance planned activities.
futuristic planning: Planning for that period which extends beyond the planning horizon in the form of future expected conditions which may exist in respect of the entity, products/services and environment but which cannot usefully be expressed in quantified terms. An example would be working out the actions needed in a future with no motor cars.
strategic planning: Formulation, evaluation and selection of strategies for the purpose of preparing a long-term plan of action to attain objectives. Also known as corporate planning and long-range planning.
tactical planning: Planning the utilisation of resources to achieve specific objectives in the most effective and efficient way.
planning horizon
Furthest time ahead for which plans can be quantified. It need not be the planning period.
See futuristic planning (planning).
planning period
Period for which a plan is prepared and used. It differs according to the product or process life cycle. For example, forestry requires a period of many years whereas fashion garments require only a few months.
policy
Undated, long-lasting and often unquantified statement of guidance regarding the way in which an organisation will seek to behave in relation to its stakeholders.
Porter's five forces
External influences upon the extent of actual and potential competition within any industry which in aggregate determine the ability of firms within that industry to earn a profit.
See Figure 2.5.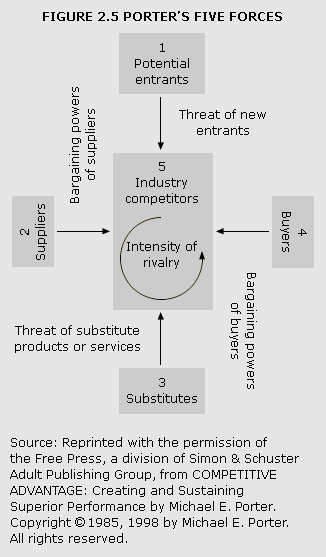
Porter's diamond
See national competitive advantage.
position audit
Part of the planning process which examines the current state of the entity in respect of: resources of tangible and intangible assets and finance; products, brands and markets; operating systems such as production and distribution; internal organisation; current results; and returns to stockholders.
post-employment benefit plans
Formal or informal arrangements under which an entity provides post-employment benefits for its employees (refer to IAS 19).
post-employment benefits
Employee benefits (other than termination benefits) which are payable after the completion of employment (IAS 19).
potential ordinary share
Financial instrument or other contract that may entitle its holder to ordinary shares (IAS 33).
pre-acquisition profits/losses
Profits or losses of a subsidiary attributable to a period prior to acquisition of control by the parent.
preferred creditors
Creditors entitled to full satisfaction of their claims in insolvency before other claims are met.
presentation currency
Currency in which the reporting entity's financial statements are presented (IAS 21).
present value
Cash equivalent now of a sum receivable or payable at a future date.
See Figure 4.1.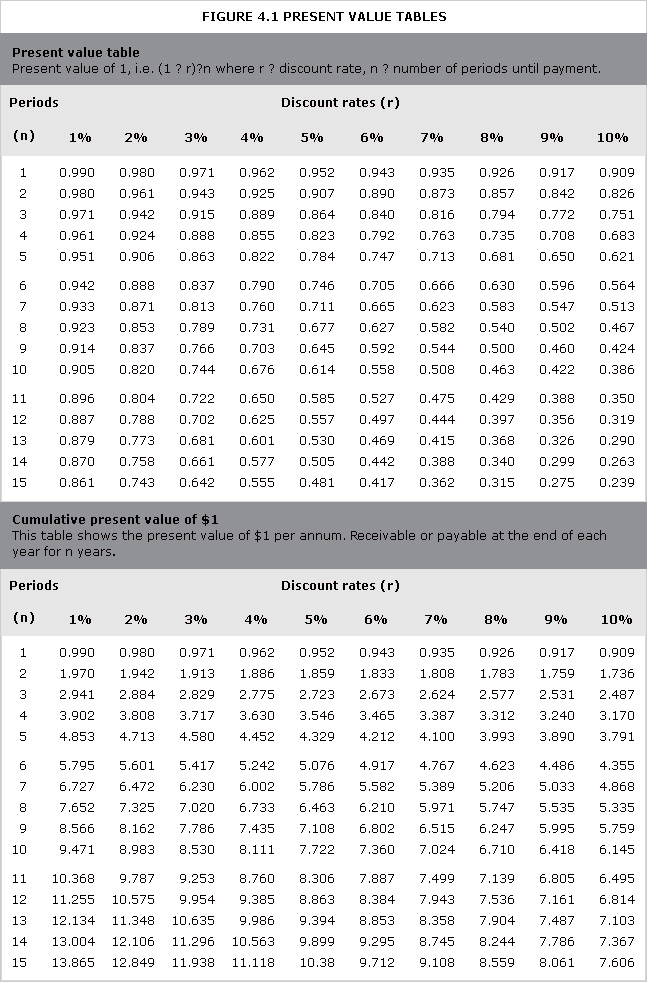
previous GAAP
Generally accepted accounting practice that a first-time adopter used immediately before adopting IFRSs (IFRS 1).
pricing
Determination of a selling price for the product or service produced. A number of methodologies may be used including:
competitive pricing: Setting a price by reference to the prices of competitive products.
cost plus pricing: Determination of price by adding a mark-up, which may incorporate a desired return on investment, to a measure of the cost of the product/service.
dual pricing: Form of transfer pricing in which the two parties to a common transaction use different prices.
historical pricing: Basing current prices on prior period prices, perhaps uplifted by a factor such as inflation.
market-based pricing: Setting a price based on the value of the product in the perception of the customer. Also known as perceived value pricing.
penetration pricing: Setting a low selling price in order to gain market share.
predatory pricing: Setting a low selling price in order to damage competitors. May involve dumping, i.e. selling a product in a foreign market at below cost, or below the domestic market price (subject to, for example, adjustments for taxation differences, transportation costs, specification differences).
premium pricing: Achievement of a price above the commodity level, due to a measure of product or service differentiation.
price skimming: Setting a high price in order to maximise short-term profitability, often on the introduction of a novel product.
range pricing: Pricing of individual products such that their prices fit logically within a range of connected products offered by one supplier, and differentiated by a factor such as weight of pack or number of product attributes offered.
selective pricing: Setting different prices for the same product or service in different markets. Can be broken down as follows:
- category pricing: Cosmetically modifying a product such that the variations allow it to sell in a number of price categories, as where a range of 'brands' are based on a common product.
- customer group pricing: Modifying the price of a product or service so that different groups of consumers pay different prices.
- peak pricing: Setting a price which varies according to level of demand.
- service level pricing: Setting a price based on the particular level of service chosen from a range.
- time material pricing: A form of cost-plus pricing in which price is determined by reference to the cost of the labour and material inputs to the product/ service.
primary financial instruments
Financial instruments such as receivables, payables and equity securities that are not derivative financial instruments (IAS 32).
prior period errors
Omission from, and misstatements in, the entity's financial statements for one or more periods arising from a failure to use, or misuse of, reliable information that was available when the financial statements for those periods were authorised for issue. Such errors include the effects of mathematical mistakes in applying accounting policies, oversights or misinterpretation of facts and fraud (IAS 8).
private company
Company which has not been registered as a public company under the UK Companies Act 1985. The major practical distinction between a private and public company is that the former may not offer its securities to the public.
See public company.
private finance initiative (PFI)
UK Policy designed to harness private sector management and expertise in the delivery of public services. Under PFI, the public sector does not buy assets, it buys the asset-based services it requires, on contract, from the private sector, the latter having the responsibility for deciding how to supply these services, the investment required to support the services and how to achieve the required standards.
private placement
Issue of shares sold to one or to a limited number of investors, rather than being offered to the market.
See placing.
probability
Likelihood of an event or a state of nature occurring, being measured in a range from 0 (no possibility) to 1 (certainty).
product bundling
Form of discounting in which a group of related products is sold at a price which is lower than that obtainable by the consumer were the products to be purchased separately.
product life cycle
Period which begins with the initial product specification and ends with the withdrawal from the market of both the product and its support. It is characterised by defined stages including growth, development, introduction, maturity, decline and abandonment (CAM-I adapted).
profit
Residual amount that remains after expenses (including capital maintenance adjustments where appropriate) have been deducted from income (IASB framework).
profit and loss account
See income statement.
profit margin
(sales – cost of sales)
This can be expressed either as a value or as a percentage of sales value. The profit margin may be calculated at different stages, hence the terms gross and net profit margin. The level of profit reported is also influenced by the extent of the application of accounting conventions, and by the method of product costing used, for example marginal or absorption costing.
profit sharing
Allocation of a proportion of company profit to stakeholders, for example employees, by an issue of shares or other means.
profit-volume/contribution graph
Graph showing the effect on contribution and on overall profit of changes in sales volume or value.
See Figure 1.6.
profitability index
![]()
Used in investment appraisal. Represents the net present value of each $1 invested in a project.
Programming
dynamic programming: Operational research technique used to solve multi-stage problems in which the decisions at one stage are the accepted assumptions applicable to the next stage.
linear programming: Series of linear equations used to construct a mathematical model. The objective is to obtain an optimal solution to a complex operational problem, which may involve the production of a number of products in an environment in which there are many constraints.
non-linear programming: Process in which the equations expressing the interactions of variables are not all linear but may, for example, be in proportion to the square of a variable.
project costing
See contract costing (cost accounting for cost objects).
projection
Expected future trend pattern obtained by extrapolation. It is principally concerned with quantitative factors, whereas a forecast includes judgements.
See Figure 2.6.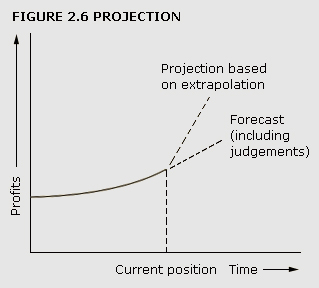
project management
Integration of all aspects of a project, ensuring that the proper knowledge and resources are available when and where needed, and above all to ensure that the expected outcome is produced in a timely, cost-effective manner. The primary function of a project manager is to manage the trade-offs between performance, timeliness and cost.
property, plant and equipment
Tangible items (non-current assets) held for use in the production or supply of goods or services for rental to others or other administrative purposes and expected to be used during more than one period (IAS 16).
proportionate consolidation—joint ventures
Method of accounting whereby a venturer's share of each of the assets, liabilities, income and expenses of a jointly controlled entity is combined with similar items, or reported as a separate line, in the venturer's financial statements (IAS 31).
prospective application
Applying a new accounting policy to transactions, other events and conditions occurring after the date at which the policy is changed and recognising the effect of the change in accounting estimates in the current and any future periods affected by the change (IAS 8).
prospectus
Description of a company's operations, financial background, prospects and the detailed terms and conditions relating to an offer for sale or placing of its shares by notice, circular, advertisement or any form of invitation which offers securities to the public.
provision
Liability of uncertain timing or amount (IAS 37).
public company
UK Company limited by shares or by guarantee, with a share capital, whose memorandum of association states that it is public and that it has complied with the registration procedures for such a company. A public company is distinguished from a private company in the following ways:
- a minimum issued share capital of 50,000;
- public limited company or plc at the end of the name;
- public company clause in the memorandum; and
- freedom to offer securities to the public.
See private company.
purchase method
Method of consolidation that views a business combination from the perspective of the acquirer who purchases a controlling interest in the net assets of the acquiree. According to IFRS 3, all business combinations should be accounted for by applying the purchase method.
purchasing power parity
Theory stating that the exchange rate between two currencies is in equilibrium when the purchasing power of currency is the same in each country. If a basket of goods costs 100 in the UK and $150 for an equivalent in the US, for equilibrium to exist, the exchange rate would be expected to be 1 = $1.50. If this were not the case, arbitrage would be expected to take place until equilibrium was restored.
put option
Option to sell a specified underlying asset at a specified exercise price on, or before, a specified exercise date.
See call option and option.
qualitative factors
Factors that are relevant to a decision but are not expressed numerically.
quality assurance
Ensuring products or services consistently meet quality specifications.
quantitative factors
Factors that are relevant to a decision and are expressed numerically.
quasi-subsidiary
Company, trust, partnership or other vehicle that, though not fulfilling the definition of a subsidiary, is directly or indirectly controlled by the reporting entity and gives rise to benefits for that entity that are in substance no different from those that would arise were the vehicle a subsidiary. Typically used in the UK (refer to FRS 5).
ratio, accounting rate of return

Sometimes used in investment appraisal, derived in the same way as return on investment. Unlike net present value and internal rate of return, the ratio is based on profits not cash flows. Exclusive use of this ratio is not recommended.
ratio, asset cover

Indicates the safety of lenders' money. Net tangible assets are usually calculated after deducting trade payables (hence, net).
ratio, asset value per share
![]()
Shows the value of net assets per share and may aid investment and disinvestment decisions. Note that this ratio is equivalent to net worth per share.
ratio, bad debts
![]()
Numerator and denominator should relate to the same period, bad debts should be calculated as an average figure for the relevant time period.
Indicates the significance of bad debts as a proportion of debtors.
ratio, capacity
Capacity is usually measured in standard units, typically standard labour or machine hours in manufacturing, and, correspondingly, standard hours in professional practices such as accountants and consultants. The more commonly used capacity levels are:
full capacity: Output achievable if sales orders, supplies, workforce, for example, were all available.
practical capacity: Full capacity less an allowance for known, unavoidable volume losses.
budgeted capacity: Standard hours planned for the budget period, taking account of, for example, budgeted sales, workforce and expected efficiency.
normal capacity: Measure of the long-run average level of capacity that may be expected. This is often used in setting the budgeted fixed overhead absorption rate (giving it stability over time, although budgeted fixed overhead volume variances may be produced as a consequence). On the following given data, the related ratios are set out below:

Indicates the budgeted shortfall in capacity as a proportion of practical capacity.
production volume ratio:
Shows the actual output as a proportion of budgeted output.
production efficiency ratio:

Measures the relationship between output produced and productive time taken, which may be measured in either direct labour or machine hours, as appropriate.
ratio, capital turnover

Expresses the number of times that capital is covered by sales in a year or the revenue generated by each $1 of capital employed. Capital employed is usually calculated as either: (a) total net assets (fixed assets + current assets - current liabilities) or (b) capital employed (equity + long-term debt). The two methods are equivalent.
ratio, contribution per unit of limiting factor

Used in short-term decision making to measure the contribution to fixed overhead and profit generated by the use of each unit of limiting factor. This is used to rank alternative uses of the limiting factor.
ratio, contribution to sales

Of particular use in product profit planning and as a means of ranking alternative products. Also important in breakeven problems that assume a constant product mix. Note, although contribution to sales ratio can be used to rank products, it cannot be used to solve limiting factor problems (unless the limiting factor is sales revenue).
ratio, creditor days
See ratio, payables days.
ratio, debtor days
See ratio, receivables days.
ratio, dividend cover
![]()
Indicates the number of times the profits attributable to the equity shareholders cover the net dividends payable for the period.
ratio, dividend payout

Shows the proportion of earnings distributed to ordinary shareholders as dividends. Indicates how safe the dividend is (as does the dividend cover ratio).
ratio, fixed asset turnover
![]()
Indicates the revenue generated by each $1 of fixed assets, or the number of times fixed assets are turned over in the year.
ratio, gearing/leverage
Relates to financial gearing, which is the relationship between an entity's borrowings, which includes both prior charge capital, for example preference shares, and long-term debt, and its share-holders' funds (ordinary share capital plus reserves). Gearing calculations can be made in a number of ways, and may be based on capital values or on earnings/interest relationships. Overdrafts and interest paid thereon may also be included.
Shows the effect of interest on the operating profit (income gearing).
See also ratio, interest cover.![]()
Shows the proportion of long-term financing which is being supplied by debt (balance sheet gearing).
A measure of the capacity to redeem debt obligations by the sale of assets.
Measures ability to redeem debt. An entity with a high proportion of prior charge capital to shareholders' funds is high geared, and is low geared if the reverse situation applies.
ratio, gross profit to sales revenue (gross profit margin %)
![]()
Used to gain an insight into the relationship between production/purchasing costs and sales revenues.
ratio, interest cover

Used by lenders to determine vulnerability of interest payments to a drop in profit.
ratio(s), inventory days
number of days' inventory:
Number of days' inventory at the forecast or recent usage rate. Can be applied to finished goods, raw material and work in progress by using appropriate numerators and denominators.
number of weeks' inventory: The efficiency of inventory utilisation is indicated by: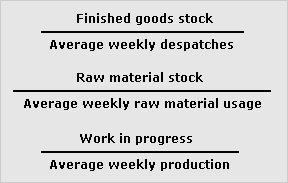
These ratios are normally calculated using appropriate values although, in certain circumstances, quantities may be used.
ratio, length of order book

The sales value of production may be based on planned, current or available capacity production.
ratio(s), liquidity
Relate to working capital and indicate the ability to meet liabilities from assets available. The most commonly used are:
acid test/quick ratio:
Indicates the ability to pay creditors in the short term.
current ratio:
An overall measure of liquidity.
ratio, margin of safety
![]()
Indicates the percentage by which forecast revenue exceeds or falls short of that required to break even.
ratio, net profit to sales revenue (net profit margin %)
![]()
A key profitability ratio. If the numerator is not multiplied by 100 it shows the profit generated by each $1 of sales.
ratio, payables days

Indicates the average time taken, in calendar days, to pay for supplies received on credit. Adjustment is needed if the ratio is materially distorted by value added or other taxes.
ratio, price/earnings (P/E ratio)

Shows the number of years it would take to recoup an equity investment from its share of the attributable profit. The P/E ratio values the shares of the company as a multiple of current or prospective earnings. The P/E ratio is the most common way of reporting the relationship between earnings and share prices, although its inverse, the earnings yield, is probably intuitively easier to grasp. A low P/E ratio implies a high earnings yield. A low P/E ratio might indicate that the market perceives earnings to be 'low quality'.
ratio, profit per employee

Indication of the effectiveness of the employment of staff. When there are full- and part-time employees, full-time equivalents should be used.
See sales per employee.
ratio pyramid
The analysis of a primary ratio into mathematically linked secondary ratios. For example:
Ratio a = b x c. Ratios b and c can be analysed by further ratios if desired. The pyramid continues with further analysis of the secondary ratios.
See Figures 1.21, 1.22 and 1.23.
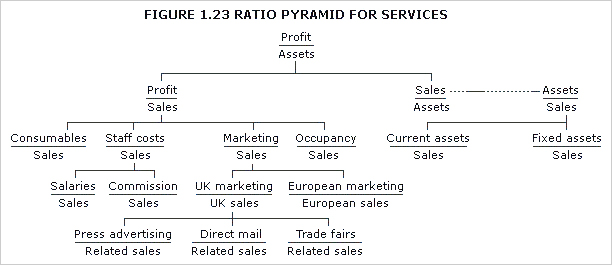
ratio, receivables days

Indicates the average time taken, in calendar days, to receive payment from credit customers. Adjustment is needed if the ratio is materially distorted by value added or other taxes.
ratio, sales per employee

Indicator of labour productivity.
See profit per employee.
ratio, stock turnover
See ratio, inventory days.
real interest rate
Interest rate approximately calculated by adjusting the nominal or money interest rate for the rate of inflation. It, therefore, represents the rate of interest in the absence of inflation.
real option
Right, but not the obligation, to take different courses of action (for example defer, abandon and expand) with respect to real assets (for example an oil well, a new product or an acquisition) as opposed to an option on financial securities or commodities.
receipts and payments account
Report of cash transactions during a period. It is used in place of an income and expenditure account when it is not considered appropriate to distinguish between capital and revenue transactions or to include accruals.
receivables
Monetary amount owed by a person or organisation to the entity as a consequence of the sale of goods or services, known as trade receivables in IASs.
receivership
Under the control of a receiver, who is appointed by secured creditors or by the court to take control of company property. The most usual reason for the appointment of a receiver is the failure of a company to pay principal sums or interest due to debenture holders whose debt is secured by fixed or floating charges over the assets of the company.
reciprocal cost allocation
Method of reallocating (strictly apportioning) service centre costs in a number of iterations until all service costs have been recharged to user centres. Can also be formulated as a set of equations and solved by matrix algebra.
See re-apportion (apportioning).
recognition
The process of incorporating in the balance sheet or income statement an item that meets the definition of an element of financial statements and satisfies the following criteria: (a) it is probable that any future economic benefit associated with the item will flow to or from the entity; and (b) the item has a cost or value that can be reliably measured (IASB framework).
recourse
Source of redress should a debt be dishonoured at maturity.
recoverable amount
Higher of an asset's (or a cash generating unit's) fair value less costs to sell and its value in use (IAS 36).
recovery
See overhead absorption rate.
redemption
Repayment of the principal amount (for example, a bond) at the date of maturity.
redemption yield
Rate of interest at which the total of the discounted values of any future payments of interest and capital is equal to the current price of a security.
regulated price
Selling price set within guidelines laid down by a regulatory authority, normally governmental.
rejects/defects
Units of output which fail a set quality standard and are subsequently rectified, sold as substandard or disposed of as scrap.
related parties
A party is a related party of an entity if it complies with one or more of the following conditions: (a) directly or indirectly through intermediaries, it controls or is controlled by or is under common control with the entity (this includes parent, subsidiaries and fellow subsidiaries); (b) it has an interest in the entity that gives it significant influence or joint control over the entity (this includes associates and joint ventures); (c) it is a member of the key management personnel of the entity or its parent; (d) it is a close member of the family of any individual noted above; and (e) it is a post-employment benefit plan for the benefit of the employees of the entity or of any entity that is itself a related party (summarised from IAS 24).
related party transaction
Transfer of resources, services or obligations between related parties, regardless of whether a price is charged (IAS 24).
relevant costs/revenues
Costs and revenues appropriate to a specific management decision. These are represented by future cash flows whose magnitude will vary depending upon the outcome of the management decision made. If stock is used, the relevant cost, used in the determination of the profitability of the transaction, would be the cost of replacing the stock, not its original purchase price, which is a sunk cost.
Abandonment analysis, based on relevant cost and revenues, is the process of determining whether or not it is more profitable to discontinue a product or service than to continue it.
relevant range
Activity levels within which assumptions about cost behaviour in breakeven analysis remain valid.
re-order level
Level of stock at which a replenishment order should be placed. Traditional optimising systems use a variation on the following computation, which builds in a measure of safety stock and minimises the likelihood of a stock-out. (maximum usage x maximum lead time)
replacement price
Price at which identical goods or capital equipment could be purchased at the date of valuation.
reporting entity
Entity for which there are users who rely on the financial statements for information about the entity that will be useful to them for making decisions about resource allocation. A reporting entity can be a single entity or a group comprising a parent and all of its subsidiaries (refer to IASB framework and IFRS 3).
research
Original and planned investigation undertaken with the prospect of gaining new scientific or technical knowledge and understanding (IAS 38).
reserves
Retained profits or surpluses. In a not-for-profit entity they are described as accumulated funds.
residual income
Profit minus a charge for capital employed in the period. The calculation is exactly the same as that for economic value added. However, in the latter case, accounting profit is often adjusted before the calculation of economic value added.
See economic value added.
residual value—intangible asset
Estimated amount which an entity would currently obtain from disposal of the asset, after deducting the expected costs of disposal, if the asset were already of the age and condition expected at the end of its useful life (IAS 38).
residual value—tangible asset
Net amount which an entity expects to obtain for an asset at the end of its useful life after deducting the expected costs of disposal (IAS 16).
resource accounting
System of accruals accounting introduced by the UK government to replace its previous cash accounting base.
restructuring
Programme that is planned and controlled by management, and materially changes either the scope of a business undertaken by an entity or the manner in which that business is conducted (IAS 37).
retention money or payments withheld
Agreed proportion of a contract price withheld for a specified period after contract completion as security for fulfilment of obligations.
retirement benefit plans
Arrangements whereby an entity provides benefits for its employees on or after termination of service (either in the form of annual income or as a lump sum or both) when such benefits, or the employer's contribution towards them, can be determined or estimated in advance of retirement (IAS 26).
retrospective application
Applying a new accounting policy to transactions, other events and conditions as if that policy had always been applied (IAS 8).
revalued amount of an asset
Fair value of an asset at the date of a revaluation, less any subsequent accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses (IAS 16).
revolving credit
A credit facility which allows the borrower, within an overall credit limit and for a set period, to borrow or repay debt as required.
return on capital employed (ROCE)

Indicates the productivity of capital employed. The denominator is normally calculated as the average of the capital employed at the beginning and the end of the year. Problems of seasonality, new capital introduced or other factors may necessitate taking the average of a number of periods within the year. The ROCE is known as the primary ratio in a ratio pyramid.
See capital employed.
return on equity

Form of return on capital employed which measures the return to the owners on their investment in an entity.
return on investment (ROI)

Often used to assess managers' performance. Managers are responsible for all assets (normally defined as non-current assets plus net current assets).
See ratio, capital turnover.
return on sales
See profit margin.
revenue
Gross inflow of economic benefits during the period arising in the course of the ordinary activities of an entity when those inflows result in increases in equity, other than increases relating to contributions from equity holders (IAS 18).
revenue expenditure
Expenditure on the manufacture of goods, the provision of services or on the general conduct of the entity which is charged to the income statement in the period the expenditure is incurred. This will include charges for depreciation and impairment of non-current assets as distinct from the cost of the assets.
See capital expenditure.
reverse acquisition
Acquisition where the acquirer is the entity whose equity interests have been acquired and the issuing entity is the acquiree. For example, a private entity arranges to have itself acquired by a smaller public entity as a means of obtaining a stock exchange listing (IFRS 3).
reverse engineering
Decomposition and analysis of competitors' products in order to determine how they are made, costs of production and the way in which future development may proceed.
revolving credit
A credit facility which allows the borrower, within an overall credit limit and for a set period, to borrow or repay debt as required.
rights issue
Raising of new capital by giving existing shareholders the right to subscribe to new shares in proportion to their current holdings. These shares are usually issued at a discount to market price. A shareholder not wishing to take up a rights issue may sell the rights.
See bonus/scrip issue.
risk
Condition in which there exists a quantifiable dispersion in the possible outcomes from any activity. Risk can be classified in a number of ways.
risk, business/operational
Relating to activities carried out within an entity, arising from structure, systems, people, products or processes.
risk, country
Associated with undertaking transactions with, or holding assets in, a particular country. Sources of risk might be political, economic or regulatory instability affecting overseas taxation, repatriation of profits, nationalisation or currency instability.
risk, environmental
Occurring due to changes in political, economic, sociocultural, technological, environment and legal factors.
risk, financial
Relating to the financial operation of an entity and includes:
credit risk: Possibility that a loss may occur from the failure of another party to perform according to the terms of a contract.
currency risk: Risk that the value of a financial instrument will fluctuate due to changes in foreign exchange rates (IAS 32).
interest rate risk: Risk that interest rate changes will affect the financial well-being of an entity.
liquidity risk: Risk that an entity will encounter difficulty in realising assets or otherwise raising funds to meet commitments associated with financial instruments—this is also known as funding risk.
risk management
Process of understanding and managing the risks that the entity is inevitably subject to in attempting to achieve its corporate objectives. For management purposes, risks are usually divided into categories such as operational; financial; legal compliance; information and personnel. One example of an integrated solution to risk management is enterprise risk management.
risk management, enterprise (ERM)
Process effected by an entity's board of directors, management and other personnel, applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risk to be within its risk appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives (Enterprise Risk Management—Integrated Framework COSO, 2004).
risk, market/systematic
Risk that cannot be diversified away, also known as systematic risk, which is measured by beta. Non-systematic or unsystematic risk applies to a single investment or class of investments, and can be reduced or eliminated by diversification.
See market risk premium and beta factor.
risk, reputation
Damage to an entity's reputation as a result of failure to manage other risks.
rolling forecast
Continuously updated forecast whereby each time actual results are reported, a further forecast period is added and intermediate period forecasts are updated.
See budget, rolling/continuous.
sale and leaseback transaction
Sale of an asset to the lessor and the subsequent leasing back of the asset under an operating lease or a finance lease. The lease payments and the sale price are usually interdependent because they are negotiated as a package (IAS 17).
Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX)
Act passed by US Congress in response to corporate accounting scandals 'to protect investors by improving the accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures made pursuant to the securities laws and for other purposes'.
scrap
Discarded material having some value.
scrip dividend
Dividend paid by the issue of additional company shares, rather than by cash.
Section 404 of SOX
Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act: Management Assessment Of Internal Controls requires each annual report of an issuer to contain an internal control report, which should
(a) state the responsibility of management for establishing and maintaining an adequate internal control structure and procedures for financial reporting; and (b) contain an assessment, as of the end of the issuer's fiscal year, of the effectiveness of the internal control structure and procedures of the issuer for financial reporting.
These internal control reports are subject to audit. Each registered public accounting firm that prepares or issues the audit report for the issuer shall attest to, and report on, the assessment made by the management of the issuer. An attestation made under this section shall be in accordance with standards for attestation engagements issued or adopted by the board. An attestation engagement shall not be the subject of a separate engagement.
secured creditors
Creditors whose claims are wholly or partly secured on the assets of a business.
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
US Commission whose purpose is to protect investors and maintain the integrity of the securities markets. It does this by requiring public companies to disclose meaningful financial and other information to the public. The SEC also oversees other participants in the securities markets such as stock exchanges, broker-dealers, investment advisors, mutual funds, and public utility holding companies. The SEC is also an enforcement authority bringing four to five hundred civil actions each year against individuals and organisations which break securities laws, through insider trading, accounting fraud, or providing false or misleading information about securities or issuers.
securitisation
Conversion of financial or physical assets into financial instruments that can be traded, often through the use of special purpose vehicles.
seed money
Equity investment into a new business by venture capitalists in order to finance the period of start-up and/or early trading. The provision of the (high-risk) seed money enables the new business to become established, such that it can ultimately raise equity on an established exchange, at which time venture capitalists would expect to realise their holding of shares, in so doing hoping to make a significant capital gain.
segment reports
Reports within the financial statements that analyse revenue, profit from operations, total assets and total liabilities by reportable segments. The segments may be by business activity or geographic area (refer to IAS 14).
See Figure 3.7.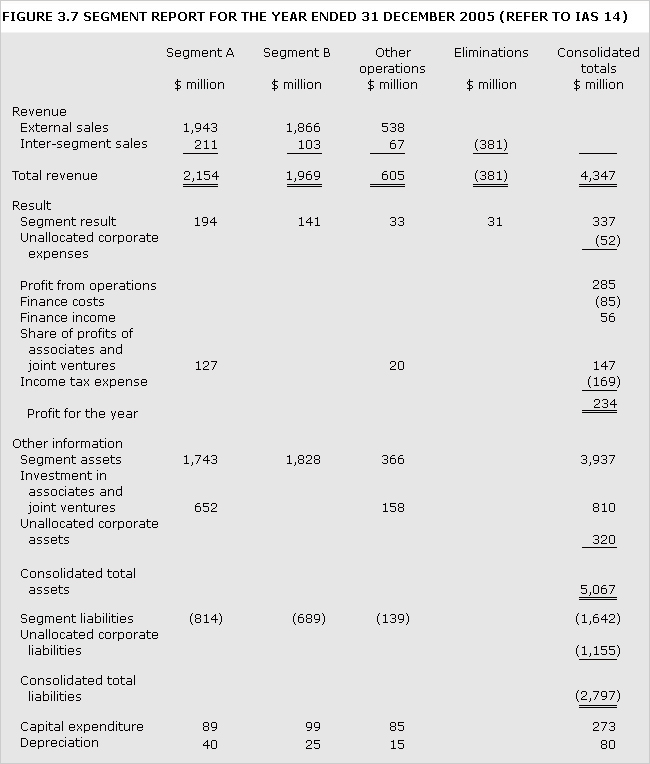
sensitivity analysis
Modelling and risk assessment procedure in which changes are made to significant variables in order to determine the effect of these changes on the planned outcome. Particular attention is thereafter paid to variables identified as being of special significance.
service level agreement
Contract between service provider and customer which specifies in detail the level of service to be provided over the contract period (for example quality, frequency, flexibility, charges) as well as the procedures to be implemented in the case of default.
shadow price
Increase in value which would be created by having available one additional unit of a limiting resource at its original cost. This represents the opportunity cost of not having the use of the one extra unit. This information is routinely produced when mathematical programming (especially linear programming) is used to model activity.
share
Fixed identifiable unit of capital in a company (or other entity) which normally has a fixed nominal or face value, which may be quite different from its market value.
convertible share: Non-equity share such as a preference share, carrying rights to convert into equity shares on predetermined terms.
cumulative preference shares: Shares which entitle the holders to a fixed rate of dividend, and the right to have any arrears of dividend paid out of future profits with priority over any distribution of profits to the holders of ordinary share capital.
deferred/founders' shares: Special class of shares ranking for dividend after preference and ordinary shares.
non-voting shares: Shares which carry no voting rights.
ordinary shares: Equity instrument that is subordinate to all other classes of equity instrument (refer to IAS 33).
participating preference shares: Shares which entitle the holder to a fixed dividend and, in addition, to the right to participate in any surplus profits after payment of agreed levels of dividends to ordinary shareholders have been made.
preference shares: Shares carrying a fixed rate of dividend, the holders of which, subject to the conditions of issue, have a prior claim to any profits available for distribution. Preference shareholders may also have a prior claim to the repayment of capital in the event of winding up.
redeemable shares: Shares which are issued on terms which may require them to be bought back by the issuer at some future date either at the discretion of the issuer or of the holder.
share capital
authorised/nominal/registered share capital: Type, class, number and amount of the shares which a company (or other entity) may issue, as empowered by its memorandum of association.
called-up share capital: Amount which the entity has required shareholders to pay on the shares issued.
issued/subscribed share capital: The type, class, number and amount of the shares held by shareholders.
paid-up share capital: Amount which shareholders are deemed to have paid on the shares issued and called up.
uncalled share capital: Amount of the nominal value of a share which is unpaid and has not been called up by the entity.
unissued share capital: Amount of the share capital authorised but not yet issued.
shareholder value
Total return to the shareholders in terms of both dividends and share price growth, calculated as the present value of future free cash flows of the business discounted at the weighted average cost of the capital of the business less the market value of its debt.
share option
Contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to subscribe to the entity's shares at a fixed or determinable price for a specific period of time (IAS 39).
share premium
Excess received, either in cash or other consideration, over the nominal or face value of the shares issued.
share-based payment arrangement
An agreement between the entity and another party (including an employee) to enter into a share-based payment transaction which thereby entitles the other party to receive cash or other assets of the entity for amounts that are based on the price of the entity's shares (or other equity instruments) or to receive equity instruments in the entity (IFRS 2).
share-based payment transaction
Transaction in which the entity receives goods or services as consideration for equity instruments of the entity (including shares or share options) or acquires goods or services for amounts that are based on the price of the entity's shares (or other equity instruments) (IFRS 2).
short-termism
Bias towards paying particular attention to short-term performance with a corresponding relative disregard to the long-run.
significant influence
Power to participate in the financial and operating policy decisions of an entity, but not have control over those policies. This may be gained by share ownership, statute or agreement (IAS 28).
simple interest
Interest which is calculated over successive periods based only on the principal.
See compound interest.
sinking fund
Money put aside periodically to settle a liability or replace an asset. The money is invested to produce a required sum at an appropriate time.
Six Sigma
Methodology, developed by Motorola others, based on Total Quality Management, to achieve very low defect rates. The 'sigma' refers to the Greek letter used to denote standard deviation, so six sigma means that the error rate lies beyond six standard deviations from the mean. To achieve six sigma, an organisation must therefore produce not more than 3.4 defects per million products.
See total quality management.
slack variables
Amount of each resource which will be unused if a specific linear programming solution is implemented.
small and medium-sized enterprise (SME)
Classification used by policy-makers to specify which categories of enterprise are affected by regulation (for example the requirement for statutory audit) or are eligible for assistance.
See Figure 4.2. 
social cost
Tangible and intangible costs and losses sustained by third parties or the general public as a result of economic activity, for example pollution by industrial effluent.
social responsibility accounting
Identification, measurement and reporting of the social costs and benefits resulting from economic activities.
sole trader
Person carrying on business with total legal responsibility for his/her actions neither in partnership nor as a company.
SORP (Statement of Recommended Practice)
Supplement UK accounting standards, approved by the ASB, which recommend accounting practices for specialised industries or sectors, to allow for features or transactions undertaken in that particular industry or sector.
spot rate
Current rate (typically of interest or currency exchange) available in the market today.
stakeholders
Those persons and organisations that have an interest in the strategy of an organisation. Stakeholders normally include shareholders, customers, staff and the local community.
standard
Benchmark measurement of resource usage or revenue or profit generation, set in defined conditions. Standards can be set on a number of bases: (a) on an ex ante estimate of expected performance; (b) on an ex post estimate of attainable performance; (c) on a prior period level of performance by the same organisation; (d) on the level of performance achieved by comparable organisations; or (e) on the level of performance required to meet organisational objectives. Standards may also be set at attainable levels that assume efficient levels of operation, but that include allowance for normal loss, waste and machine down time, or at ideal levels that make no allowance for the above losses, and are only attainable under the most favourable conditions. The effect of different levels on staff motivation will be an important influence on the type of standards that are used.
See standard, ex ante, and standard, ex post.
standard cost card/standard product specification
Document or digital record detailing for each individual product, the standard inputs required for production as well as the standard selling price. Inputs are normally divided into labour, material and overhead categories, and both price and quantity information is shown for each.
standard direct labour cost
Planned cost of direct labour. (standard direct labour time for one unit of product x standard labour rate) There are separate calculations for different processes and/or grades of labour.
standard, ex ante
Before the event. An ex ante budget or standard is set before a period of activity commences.
standard, ex post
After the event. An ex post budget, or standard, is set after the end of a period of activity, when it can represent the optimum achievable level of performance in the conditions which were experienced. Thus the budget can be flexed, and standards can reflect factors such as unanticipated changes in technology and in price levels. This approach may be used in conjunction with sophisticated cost and revenue modelling to determine how far both the plan and the achieved results differed from the performance that would have been expected in the circumstances which were experienced.
standard hour or minute
Amount of work achievable, at standard efficiency levels, in an hour or minute.
standard performance—labour
Level of efficiency which appropriately trained, motivated and resourced employees can achieve in the long-run.
Standards Advisory Council (SAC)
Formal vehicle for groups and individuals to offer advice and feedback to the IASB regarding the implications of proposed Standards. The SAC has to be consulted on all major IASB projects.
statement of affairs
Statement, usually prepared by a receiver, in a prescribed form, showing the estimated financial position of a debtor or of a company (or other entity) which may be unable to meet its debts. It contains a summary of the debtor's assets and liabilities. The assets are shown at their estimated realisable values. The various classes of creditors, such as preferential, secured, partly secured and unsecured, are shown separately.
Statement of Auditing Standards (SAS)
A standard issued by the Auditing Practices Board (APB), containing prescriptions as to the basic principles and practices which members of the UK accountancy bodies are expected to follow in the course of an audit. Superseded from 2005 by International Standards on Auditing (UK and Ireland) (ISAs (UK and Ireland)), and International Standards on Quality Control (ISQC) issued by the IAASB.
See IAASB.
statement of changes in equity
Summary of all the component changes in equity for a period (see Figure 3.8) or a summary of changes in equity other than those arising from transactions with equity holders in their capacity as equity holders (see Figure 3.9). Refer to IAS 1.
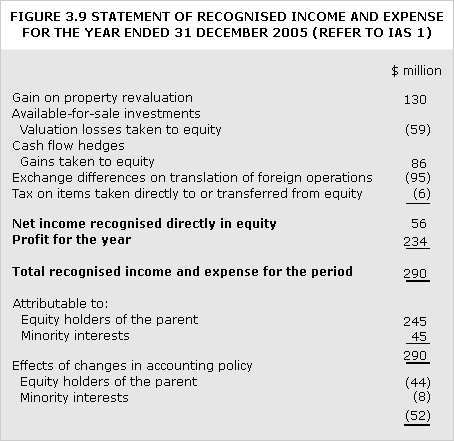
Statement of Standard Accounting Practice (SSAP)
Standard issued by the Councils of the CCAB member bodies following proposals developed by the Accounting Standards Committee. The ASC has been replaced by the ASB who adopted all the existing SSAP.
See Financial Reporting Standard.
statutory body
Entity formed by a UK Act of the Parliament.
stewardship
Responsibility of agents to act in the best interests of their principals, by keeping adequate records of transactions and by acting so as to maintain or increase both the capital and income of the principal.
stock (goods)
See inventories.
stock, buffer
Stock of materials, or of work-in-progress, maintained in order to protect user departments from the effect of possible interruptions to supply.
stock control
Systematic regulation of stock levels. Called inventory control in the US.
stock exchange
Registered market in securities.
stock, free
Stock on hand or on order which has not been scheduled for use. (physical stock + stock ordered - stock scheduled for use)
stock level, maximum
Stock level, set for control purposes, which actual stockholding should never exceed. ((reorder level + EOQ) - (minimum rate of usage x minimum lead time))
stock level, minimum
Stock level, set for control purposes, below which stockholding should not fall without being highlighted. (reorder level - (average rate of usage x average lead time))
stock, safety
Quantity of stocks of raw materials, work-in-progress and finished goods which are carried in excess of the expected usage during the lead time of an activity. The safety stock reduces the probability of operations having to be suspended.
stock (inventory) valuation
average cost: Used to price issues of goods or materials at the weighted average cost of all units held.
first-in, first-out (FIFO): Used to price issues of goods or materials based on the cost of the oldest units held, irrespective of the sequence in which the actual issue of units held takes place. Closing stock is, therefore, valued at the cost of the oldest purchases.
last-in, first-out (LIFO) Used to price issues of goods or materials based on the cost of the most recently received units. Cost of sales in the income statement is, therefore, valued at the cost of the most recent purchases. LIFO is permitted under US GAAP but is not permitted by IAS 2 (or SSAP 9 in the UK).
standard cost: All units held as stock are valued at a standard cost so that units issued and closing stock are valued at standard cost, with any variance between actual costs incurred and standard cost reported in the income statement in the period in which it is incurred. All the above methods value stock at cost, but IAS 2 requires all stocks to be valued at the lower of cost and net realisable value.
See fair value less costs to sell.
strategic business unit
Section, usually a division, within a larger organisation that has a significant degree of autonomy, typically being responsible for developing and marketing its own products and services.
strategic financial management
Identification of the possible strategies capable of maximising an entity's net present value, the allocation of scarce capital resources among the competing opportunities and the implementation and monitoring of the chosen strategy so as to achieve stated objectives.
strategic investment appraisal
Method of investment appraisal which allows the inclusion of both financial and non-financial factors. Project benefits are appraised in terms of their contribution to the strategies of the organisation either by their financial contribution or, for non-financial benefits, by the use of index numbers or other means.
See investment appraisal.
strategic management accounting
Form of management accounting in which emphasis is placed on information which relates to factors external to the entity, as well as non-financial information and internally generated information.
strategic plan
Statement of long-term goals along with a definition of the strategies and policies which will ensure achievement of these goals.
strategy
Course of action, including the specification of resources required, to achieve a specific objective.
See Figure 1.10.
strategy map/mapping
Diagram that describes how an entity creates value by linking the strategic objectives of an organisation in explicit cause and effect relationships within the four quadrants of the balanced scorecard.
subordinated debt
Ranks below other debt under the terms of the agreement between the borrower and the lender.
subsidiary
Entity, including an unincorporated entity such as a partnership, that is controlled by another entity (known as the parent) (IFRS 3).
super variable costing
See throughput accounting.
swap
Contract to exchange payments of some sort in the future.
SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis, or corporate appraisal, evaluates the strategic position of an entity within its environment. Factors identified are listed as Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities or Threats.
tableau de bord
Performance measurement approach, similar to the balanced scorecard, but developed and commonly used in France. A tableau de bord is a dashboard, such as that found in a car or aircraft. The tableau, in strategic management, sets out the various performance indicators in related groups.
tactical plan/tactics
Short-term plan for achieving an entity's objectives.
See Figure 1.10.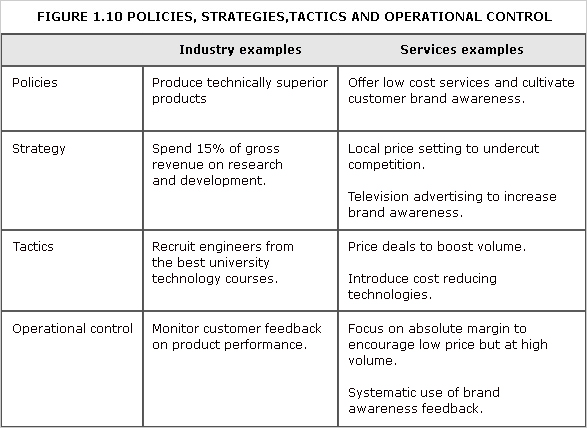
takeover
Acquisition by a company of a controlling interest in the voting share capital of another company, usually achieved by the purchase of a majority of the voting shares.
tax avoidance
Organisation of a taxpayer's affairs so that the minimum tax liability is incurred. Tax avoidance involves making the maximum use of all legal means of minimising liability to taxation
tax base (of an asset/liability)
Amount attributed to that asset or liability for tax purposes (IAS 12).
tax evasion
Minimisation of tax liability by illegal means, such as by the under-declaration of income.
taxable profit or loss
Profit or loss for a period, determined in accordance with the rules established by the taxation authorities, upon which income (corporation) taxes are payable (or recoverable) (IAS 12).
tax shield
Reduction in tax payable due to the use of tax-allowable deductions against taxable income. It is measured by the discounted value of future tax savings generated by the available tax reliefs.
technical analysis
Analysis of past movements in the prices of, amongst other things, financial instruments, currencies and commodities, with a view to, by applying analytical techniques, predicting future price movements.
See fundamental analysis.
teeming and lading
Fraud based on a continuous cycle of stealing and later replacing assets (generally cash), each theft being used in part, or in full, to repay a previous theft in order to avoid detection.
temporary difference
Difference between the carrying amount of an asset or liability in the balance sheet and its tax base. It may be either a taxable temporary difference or a deductible temporary difference (IAS 12).
temporary difference, taxable
Temporary difference that will result in taxable amounts in determining taxable profit (or loss) of future periods when the carrying amount of the asset or liability is recovered or settled (IAS 12).
termination benefits
Employee benefits payable either as a result of an entity's decision to terminate an employee's employment before the normal retirement date or an employee's decision to accept voluntary redundancy in exchange for these benefits (IAS 19).
term (of a capital instrument)
The period from the date of issue of the capital instrument to the date at which it will expire, be redeemed, or be cancelled (FRS 4).
tests of control
Tests performed to obtain audit evidence about the operating effectiveness of controls in preventing, or detecting and correcting, material misstatements at the assertion level (Glossary of terms, Auditing Standards (ISAs (UK and Ireland))).
three generic strategies
Strategies of differentiation, focus and cost leadership outlined by Porter as offering possible means of outperforming competitors within an industry, and of coping with the five competitive forces.
See Porter's five forces.
See Figure 2.7.
timing difference
Difference between the balances held on related accounts which are caused by differences in the timing of the input of common transactions, for example a direct debit will appear on the bank statement before it is entered into the bank account. Knowledge of the timing difference allows the balances on the two accounts to be reconciled.
total quality management (TQM)
Integrated and comprehensive system of planning and controlling all business functions so that products or services are produced which meet or exceed customer expectations. TQM is a philosophy of business behaviour, embracing principles such as employee involvement, continuous improvement at all levels and customer focus, as well as being a collection of related techniques aimed at improving quality such as full documentation of activities, clear goal-setting and performance measurement from the customer perspective.
theory, agency
Hypothesis that attempts to explain elements of organisational behaviour through an understanding of the relationships between principals (such as shareholders) and agents (such as entity managers and accountants). A conflict may exist between the actions undertaken by agents in furtherance of their own self-interest, and those required to promote the interests of the principals. Within the hierarchy of entities, the same goal incongruence may arise when divisional managers promote their own self-interest over those of other divisions and of the entity generally.
theory, contingency
Theory relating to the design of accounting systems that presupposes that systems can be effectively designed to suit the circumstances of the firm including its technology, entity structure and its competitive environment. For example, it is argued that mechanistic (hierarchical, bureaucratic) systems can be effective in stable environments. Organic (typically flatter, task-related) systems are said to be more appropriate in more turbulent, competitive environments.
theory of constraints (TOC)
Procedure based on identifying bottlenecks (constraints), maximising their use, subordinating other facilities to the demands of the bottleneck facilities, alleviating bottlenecks and re-evaluating the whole system. (Goldratt created this concept.)
throughput
Term defined, in work by Goldratt, as sales minus material and component costs. Similar to contribution except material is considered the only variable cost. Goldratt argues that labour costs should be treated as fixed. In Goldratt's analysis operating expense is all non-material costs and inventory cost is defined as the cost of assets employed.
throughput accounting (TA)
Variable cost accounting presentation based on the definition of throughput (sales minus material and component costs). Sometimes referred to as super variable costing because only material costs are treated as variable.
throughput per bottleneck minute
Method of ranking products that share the same (bottleneck) facility. Very similar to the use of contribution per unit of limiting factor.
throughput ratios
Several ratios were defined by Galloway and Waldron based on the definition of throughput. The TA (throughput accounting) ratio is: 
Note: Galloway and Waldron define factory cost in the same way that Goldratt defines operating expense. See throughput. If the TA ratio is greater than 1 the product in question is 'profitable' because, if all capacity were devoted to that product, the throughput generated would exceed the total factory cost. If there was a bottleneck products could be ranked by a variant of the TA ratio (although the ranking is the same as that derived by the use of throughput per bottleneck minute). Other performance ratios suggested include:
total assets
Total carrying value of all assets (non-current and current, tangible and intangible).
total shareholder return
Combined capital gain plus dividend income received by an investor over the investment period.
trade payables
See payables.
trade receivables
See receivables.
transaction exposure
Susceptibility of an entity to the effect of foreign exchange rate changes during the transaction cycle associated with the export/import of goods or services. Transaction exposure is present from the time a price is agreed until the payment has been made/received in the domestic currency.
transfer price
Price at which goods or services are transferred between different units in the same company. May be set on a number of bases, such as marginal cost, full cost, market price or negotiation. For the transfer of goods between units in different countries, tax implications mean that the respective governments have to accept the method used. They are likely to insist on arm's-length transfer prices.
translation exposure
Susceptibility of the balance sheet and income statement to the effect of foreign exchange rate changes.
See foreign currency translation.
treasury bill
Short-term money market instrument issued, used to supply the government's short-term financing needs.
treasury management
Corporate handling of all financial matters, the generation of external and internal funds for business, the management of currencies and cash flows, and the complex strategies, policies and procedures of corporate finance (Association of Corporate Treasurers).
See Figure 4.3.
treasury shares
Shares held by an entity when it re-acquires its own equity instruments. These should be deducted from equity in the balance sheet (refer to IAS 32).
turnover/sales
See revenue
uncertainty
Inability to predict the outcome from an activity due to a lack of information about the required input/output relationships or about the environment within which the activity takes place.
uniform accounting
System by which different entities in the same industry adopt common concepts, principles and assumptions in order to generate accounting information that facilitates inter-entity comparison or a system of classifying financial accounts in a similar manner within defined business sectors of a national economy to ensure comparability.
Urgent Issues Task Force (UITF)
Committee of the ASB whose aim is to assist the ASB in areas where unsatisfactory or conflicting interpretations of an accounting standard have developed, or seem likely to develop. Abstracts published by the UITF have the same legal status as accounting standards.
useful life (assets)
Estimated period over which an asset is expected to be available for use by an entity or the number of production or similar units expected to be obtained from the asset by the entity (IAS 16).
user groups
Different interest groups who may make use of publicly available financial statements. Lenders, employees, investors and competitors may be classed as separate user groups.
value added
Traditionally the difference between sales revenue and the cost of materials and bought-out services. Alternatively, it might be calculated as the sum of profit, interest and all conversion costs. Recently, more commonly used in the context of economic value added.
See economic value added.
value-added activity
Activity necessary to enhance customer perceived value in the good or service being provided. The procurement of high quality resource inputs would be a value-adding activity while activity required to correct errors would be non-value-added in nature.
value-added tax (VAT)
Tax on consumer expenditure, collected on business transactions and imports. VAT paid by all entities on inputs may be reclaimed or set against output VAT collected.
value analysis
Systematic interdisciplinary examination of factors affecting the cost of a product or service, in order to devise means of achieving the specified purpose most economically at the required standard of quality and reliability (BS 3138)1.
1 Permission to reproduce extracts from BS 3138: 1992 is granted by BSI. British Standards can be obtained from BSI Customer Services, 389 Chiswich High Road, London W4 4AL.
email: cservices@bsi_global.com.
value-based management
Management team preoccupation with searching for and implementing the activities which will contribute most to increases in shareholder value.
value chain
Sequence of business activities by which, in the perspective of the end-user, value is added to the products or services produced by an entity.
value-chain analysis
Use of the value-chain model to identify the value adding activities of an entity.
value driver
Activity or organisational focus which enhances the perceived value of a product or service in the perception of the consumer, and which therefore creates value for the producer. Advanced technology, reliability or reputation for customer care may be value drivers.
value engineering
Redesign of an activity, product or service so that value to the customer is enhanced while costs are reduced (or, at least, increase by less than the resulting price increase).
value for money
Performance of an activity in such a way as to simultaneously achieve economy, efficiency and effectiveness.
value in use
Present value of the estimated future cash flows expected to arise from the continuing use of an asset (or cash generating unit) and from its disposal at the end of its useful life (IFRS 5).
value system
Series of connected value chains belonging to the entity, its suppliers, rivals and customers.
variance
Difference between a planned, budgeted or standard cost and the actual cost incurred. The same comparisons may be made for revenues.
variance, administrative cost
Measurement of the extent of any over- or under-spend on administrative costs. (budgeted cost of administration – actual cost)
variance analysis
Evaluation of performance by means of variances, whose timely reporting should maximise the opportunity for managerial action.
See Figure 1.34.
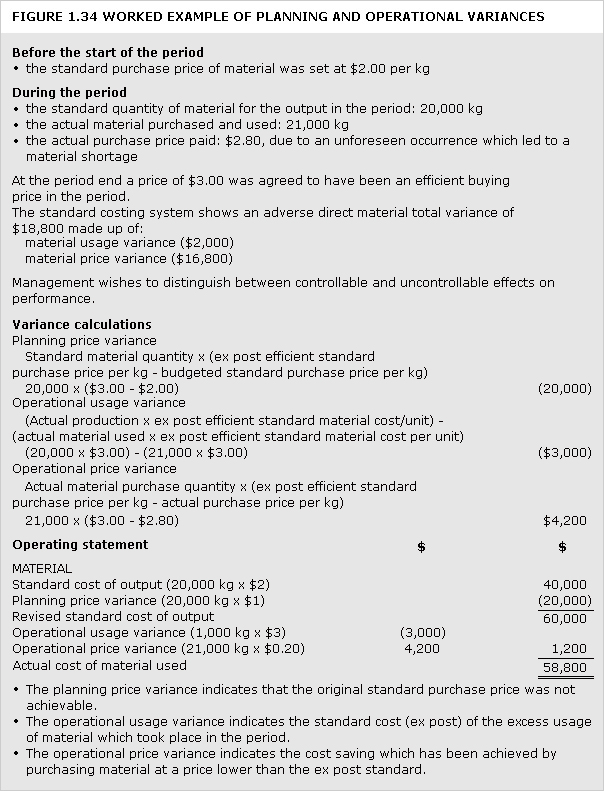
variance, budget
Difference, for each cost or revenue element in a budget, between the budgeted amount and the actual cost or revenue. Where flexible budgeting is employed, it is the difference between the flexed budget and the actual value.
variance, direct labour efficiency
Standard labour cost of any change from the standard level of labour efficiency. ((actual production in standard hours - actual hours worked) x standard direct labour rate per hour)
See Figure 1.28.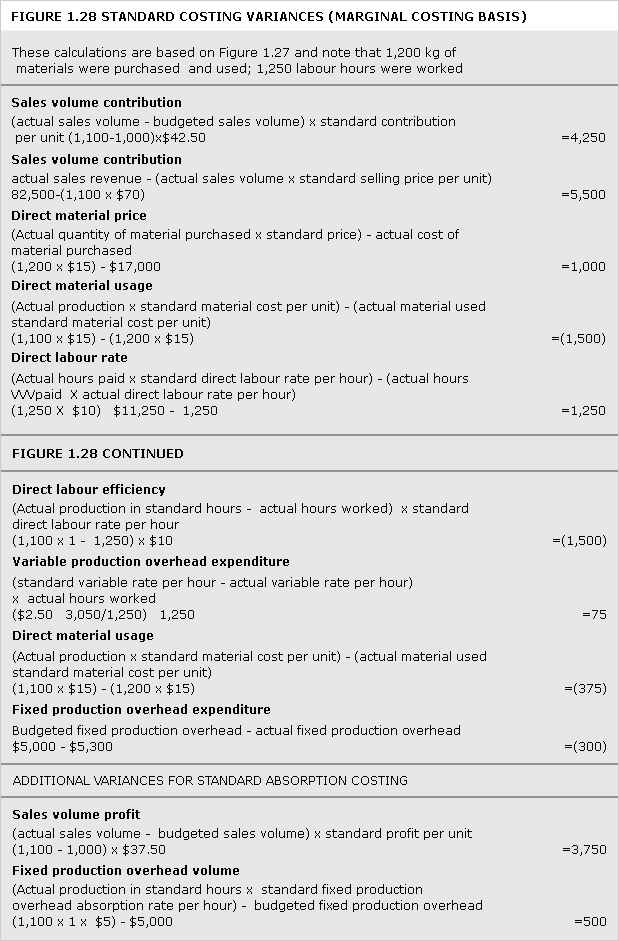
variance, direct labour idle time
This variance occurs when the hours paid exceed the hours worked and there is an extra cost caused by this idle time. Its computation increases the accuracy of the labour efficiency variance. ((hours paid - hours worked) x standard direct labour rate per hour)
variance, direct labour mix
Subdivision of the direct labour efficiency variance. If grades of labour can be substituted the mix variance measures the cost of any variation from the standard mix of grades.
((actual hours for grade - hours for grade based on total labour hours split in standard proportions) x (weighted average cost per hour - standard cost per hour))
Alternatively, the calculation can be made without reference to the relative cost of the various labour inputs.
((hours for grade based on total labour hours split in standard proportions - actual labour hours for grade) x standard cost per hour)
When the individual grade variances are summed the same total mix variance is calculated. The first method is recommended because the individual grade variances are meaningful, whereas in the second method they are not.
variance, direct labour rate
Indicates the actual cost of any change from the standard labour rate of remuneration. ((actual hours paid x standard direct labour rate per hour) - (actual hours paid x actual direct labour rate per hour))
See Figure 1.28.
variance, direct labour total
Indicates the difference between the standard direct labour cost of the output which has been produced and the actual direct labour cost incurred.
((standard hours produced x standard direct labour rate per hour) - (actual hours paid x actual direct labour rate per hour))
See Figure 1.28.
variance, direct labour yield
Subdivision of the direct labour efficiency variance. Measures the effect on cost of any difference between the actual usage of labour and that justified by the output produced. It is recommended that the variance be calculated in total and not for individual labour grade inputs.
((standard labour hours allowed for actual output - actual labour hours input) x standard weighted average cost per direct labour hour)
It may also be calculated in the following way:
((standard labour hours required for good output - actual labour hours worked in standard proportions) x standard cost per labour hour)
variance, direct material mix
Subdivision of the material usage variance. If different materials can be substituted the mix variance measures the cost of any variation from the standard mix of materials.
((actual quantity of material - quantity of material based on total material quantity split in standard proportions) x (weighted average cost per kg, litre, other - standard cost per kg, litre, other))
Alternatively, the calculation can be made without reference to the relative cost of the various material inputs.
((quantity of material based on total material quantity split in standard proportions - actual quantity of material) x standard cost per kg, litre, other)
When the individual material variances are summed the same total mix variance is calculated. The first method is recommended because the individual material variances are meaningful, whereas in the second method they are not.
See Figure 1.31.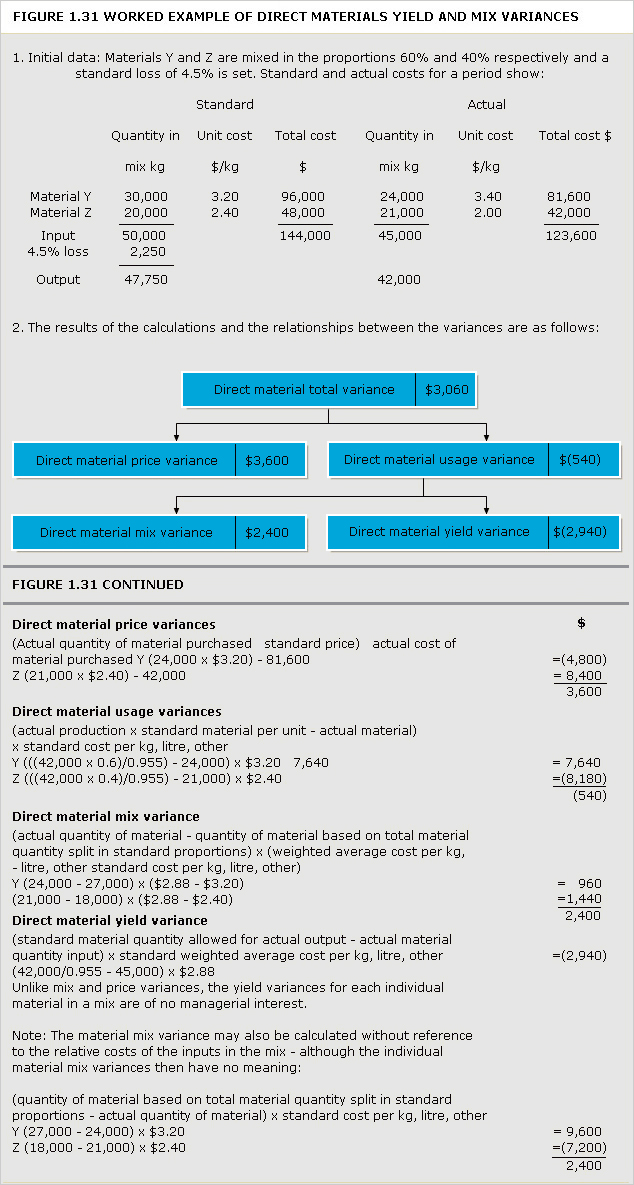
variance, direct material price
Difference between the actual price paid for purchased materials and their standard cost.
((actual quantity of material purchased x standard price) - actual cost of material purchased)
The material price variance may also be calculated at the time of material withdrawal from stores. In this case, the stock accounts are maintained at actual cost, price variances being extracted at the time of material usage rather than of purchase.
((actual material used x standard cost) - actual cost of material used)
The latter method is not usually recommended because one of the advantages of a standard costing system is the valuation of all stock at standard costs.
See Figure 1.28.

variance, direct material total
Measurement of the difference between the standard material cost of the output produced and the actual material cost incurred.
(standard material cost of output produced x actual cost of material purchased)
Where the quantities of material purchased and used are different, the total variance should be calculated as the sum of the usage and price variances.
variance, direct material usage
Measures efficiency in the use of material, by comparing standard material usage for actual production with actual material used, the difference is valued at standard cost.
((actual production x standard material per unit - actual material usage) x standard cost per kg, litre, other)
The direct material usage variance may be divided into mix and yield variances if several materials are mixed in standard proportions.
See Figure 1.28.
variance, direct material yield
Subdivision of the material usage variance. Measures the effect on cost of any difference between the actual usage of material and that justified by the output produced. It is recommended that the variance be calculated in total and not for individual material inputs.
((standard material quantity allowed for actual output - actual material quantity input) x standard weighted average cost per kg, litre, other)
It may also be calculated in the following way:
((standard material quantity required for actual output - actual material quantities used in standard proportions) x standard cost per kg, litre, other)
See Figure 1.31.

variance, fixed production overhead capacity
Little used subdivision of the fixed production overhead volume variance.
variance, fixed production overhead efficiency
Little used subdivision of the fixed production overhead volume variance.
variance, fixed production overhead expenditure
The difference between the fixed production overhead which should have been incurred in the period, and that which was incurred. (budgeted fixed production overhead - actual fixed production overhead)
variance, fixed production overhead total
The difference between the fixed production overhead absorbed by actual production and the actual fixed production overhead incurred.
((actual production in standard hours x fixed production overhead absorption rate per hour) - actual fixed production overhead)
This variance can be divided into fixed production overhead expenditure and fixed production overhead volume variances.
variance, fixed production overhead volume
A measure of the over- or under-absorption of overhead cost caused by actual production volume differing from that budgeted.
((actual production in standard hours x fixed production overhead absorption rate per hour) - budgeted fixed production overhead)
See Figure 1.28.

variance, joint
A variance which is caused by both the prices and quantities of inputs differing from the specifications in the original standard.
See Figure 1.24.
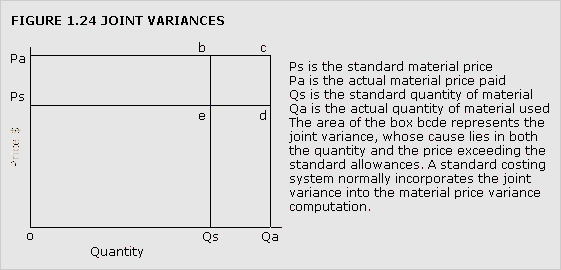
variance, market share
A subdivision of the sales volume contribution or margin variance, applicable when the actual market size of a product or product group is known. It indicates the change in contribution or margin caused by a change in market share.
((actual sales volume - sales volume based on budgeted share of actual market) x standard contribution or margin per unit)
See Figure 1.33.
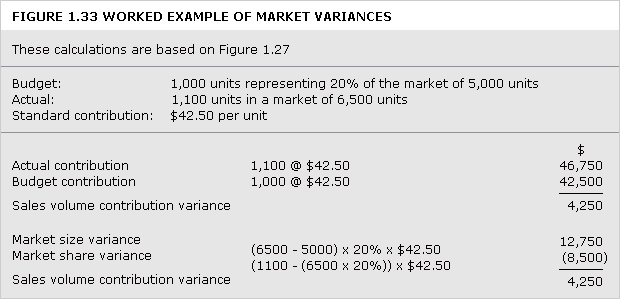
variance, market size
A subdivision of the sales volume contribution or margin variance, applicable when the actual market size of a product or product group is known. It indicates the change in contribution or margin caused by a change in the size of the market.
((sales volume based on budgeted share of actual market - budgeted sales volume) x standard contribution or margin per unit)
See Figure 1.33.

variance, marketing cost
Where marketing cost contains both fixed and variable components, separate variances should be calculated.
(budgeted marketing cost - actual marketing cost)
variance, operational
Classification of variances in which non-standard performance is defined as being that which differs from an ex post standard. Operational variances can relate to any element of the standard product specification.
See Figure 1.34.

variance, planning
Classification of variances caused by ex ante budget allowances being changed to an ex post basis. Also known as a revision variance.
See Figure 1.34.
variance, sales mix contribution/profit margin
Subdivision of the sales volume contribution/profit margin variance. The change in the contribution/profit margin caused by a change in the mix of the products or services sold.
((actual sales units - sales units based on total sales in budget proportions) x (standard contribution/profit margin per unit - budget weighted average contribution/profit margin per unit))
This method of computation highlights the contribution/profit margin effect, by product, of sales deviating from budget proportions. A favourable variance denotes either selling proportionately more of a relatively high contribution/profit margin product or proportionately less of a relatively low contribution/profit margin product. It can also be calculated as:
((actual sales units - sales units based on total sales in budget proportions) x standard contribution/profit margin per unit)
When summed up for all products this method gives the same result as the first method. The first method is recommended because the results for individual products are meaningful, whereas in the second method they are not.
See Figure 1.32
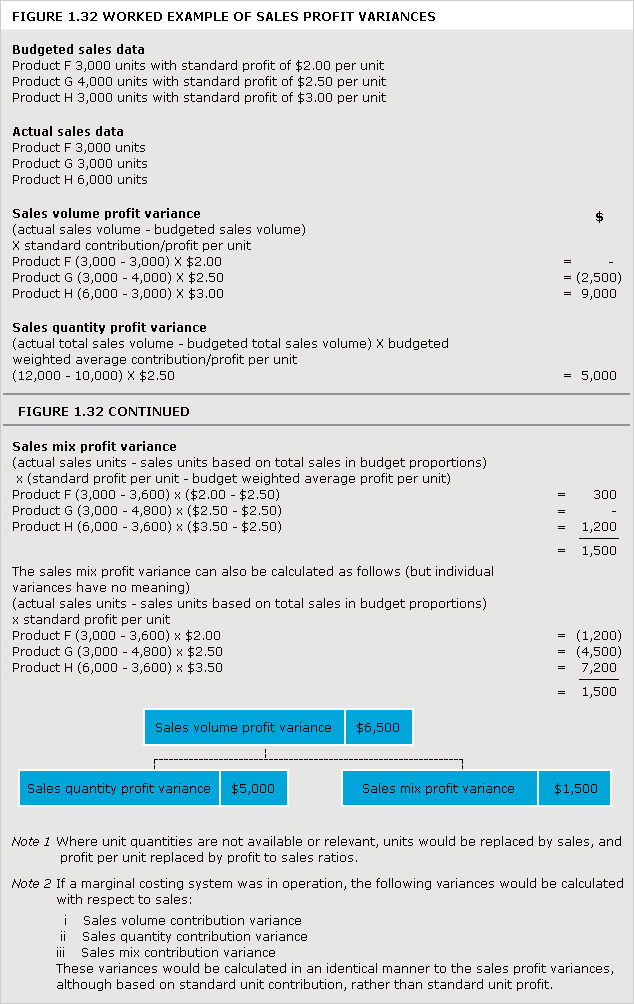
variance, sales price
Change in revenue caused by the actual selling price differing from that budgeted.
(actual sales revenue - (actual sales volume x standard selling price per unit))
See Figure 1.28.
variance, sales quantity contribution/profit
Subdivision of the sales volume contribution/ profit variance. It is relevant if there are multiple products and the actual sales mix differs from the budgeted sales mix. In these situations this variance, together with the sales mix contribution/profit variance, will comprise the sales volume contribution/profit variance (for all products). It can be calculated in either of the following ways:
((actual total sales volume - budgeted total sales volume) x budgeted weighted average contribution/profit per unit)
or
((actual total sales volume in budgeted mix - budgeted sales volume) x budgeted contribution/profit per unit)
If the second method is used the sum of the variances for all products will be the same as the result obtained using the first formula.
See Figure 1.32.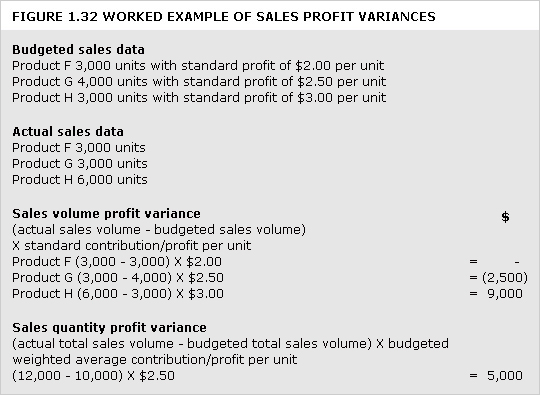
variance, sales volume contribution/profit
Measure of the effect on contribution/profit of not achieving the budgeted
volume of sales.
((actual sales volume - budgeted sales volume) x standard contribution/profit per unit)
See Figure 1.28.
variance, sales volume revenue
Change in sales revenue caused by sales volume differing from that budgeted.
((actual sales volume - budget sales) x standard selling price per unit)
This variance is logical but little used because it cannot be combined with contribution/profit variances in reconciling budget with actual contribution/profit. In principle, if several products are considered, the sales mix revenue variance and total sales volume revenue variance can be calculated.
See variance, sales mix contribution and variance, sales quantity contribution/profit for the method of derivation - substitute 'selling price' for 'contribution' in the appropriate formula.
variance, total profit
Difference between the actual profit and the profit in the budget. The total profit variance is the sum of all the subsidiary variances.
(actual profit - budgeted profit)
variance, variable production overhead efficiency
Standard variable overhead cost of any change from the standard level of efficiency.
((actual production in standard hours - actual hours worked) x standard variable overhead rate per hour)
This is directly analogous to the calculation of direct labour efficiency variance and implicitly assumes that variable overhead is recovered on a direct labour hour base. However, the formula can equally be used if variable overhead is recovered on a machine or process hour base.
See Figure 1.28.
variance, variable production overhead expenditure
Indicates the actual cost of any change from the standard rate per hour.
((standard variable rate per hour - actual variable rate per hour) x actual hours worked)
Hours refer to either labour or machine hours depending on the recovery base chosen for variable production overhead.
See Figure 1.28.
variance, variable production overhead total
Measures the difference between variable overhead that should be used for actual output and variable production overhead actually used.
((actual production in standard hours x standard variable production overhead absorption rate per hour) - actual cost incurred)
The variable production overhead efficiency and rate variances are subdivisions of this variance.
venture capital
Specialised form of finance provided for new companies, buy-outs and small growth companies which are perceived as carrying above-average risk.
venturer
Party to a joint venture that has joint control over that joint venture (IAS 31).
vision statement
See mission statement.
warrant
Financial instrument that gives the holder the right to purchase ordinary shares (IAS 33).
waste
Discarded material having no value.
wasting asset
Non-current asset which is consumed or exhausted in the process of earning income, for example a mine or quarry.
weighted average cost of capital (WACC)
The average cost of the company's finance (including equity, debentures and bank loans) weighted according to the proportion each element bears to the total pool of capital. Weighting is usually based on market valuations, current yields and costs after tax.
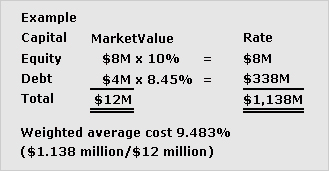
The weighted average cost of capital is often used as the measure to be used as the hurdle rate for investment decisions or as the measure to be minimised in order to find the optimal capital structure for the company.
See cost of capital.
window-dressing
Creative accounting practice in which changes in short-term funding have the effect of disguising or improving the reported liquidity position of the reporting entity.
withholding tax
Tax on dividends or other income that is deducted by the payer of the income and paid to the taxation authorities on behalf of the recipient.
working capital
Capital available for conducting the day-to-day operations of an entity, normally the excess of current assets over current liabilities.
working capital cycle
The period of time which elapses between the point at which cash begins to be expended on the production of a product, and the collection of cash from the purchaser.
world-class manufacturing
Position of international manufacturing excellence, achieved by developing a culture based on factors such as continuous improvement, problem prevention, zero defect tolerance, customer-driven JIT-based production and total quality management.
write-down
A reduction in the recorded value of an asset to comply with the concept of prudence. The valuation of stock at the lower of cost or net realisable value (SSAP 9) may require the values of some stock to be written down.
writing down allowance
A tax allowance, related to a firm's capital expenditure, which reduces profit subject to taxation.
yield curve
A diagrammatical representation of the relationship between interest rates and the maturities of a similar set of securities. An upwardly sloping interest rate curve indicates that interest rates increase as security maturities lengthen. This might indicate that investors are averse to the increased uncertainty associated with future investment, and/or that there is an expectation that interest rates will rise in the future.
Z score
A single figure, produced by a financial model, which combines a number of variables (generally financial statement ratios), whose magnitude is intended to aid the prediction of failure, that is a Z score model may predict that a company with a score of 1.8 or less is likely to fail within 12 months. Individual companies are scored against this benchmark.
zero coupon bond
A bond offering no interest payments, all investor return being gained through capital appreciation.